A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 skin cancer prevention study of {alpha}-difluoromethylornithine in subjects with previous history of skin cancer
- PMID: 20051371
- PMCID: PMC2804946
- DOI: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-09-0096
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 skin cancer prevention study of {alpha}-difluoromethylornithine in subjects with previous history of skin cancer
Abstract
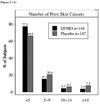
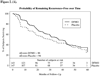
Preclinical studies have shown that the inhibition of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) by alpha-difluoromethylornithine (DFMO) and resultant decreases in tissue concentrations of polyamines (putrescine and spermidine) prevents neoplastic developments in many tissue types. Clinical studies of oral DFMO at 500 mg/m(2)/day revealed it to be safe and tolerable and resulted in significant inhibition of phorbol ester-induced skin ODC activity. Two hundred and ninety-one participants (mean age, 61 years; 60% male) with a history of prior nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC; mean, 4.5 skin cancers) were randomized to oral DFMO (500 mg/m(2)/day) or placebo for 4 to 5 years. There was a trend toward a history of more prior skin cancers in subjects randomized to placebo, but all other characteristics including sunscreen and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use were evenly distributed. Evaluation of 1,200 person-years of follow-up revealed a new NMSC rate of 0.5 events/person/year. The primary end point, new NMSCs, was not significantly different between subjects taking DFMO and placebo (260 versus 363 cancers, P = 0.069, two-sample t test). Evaluation of basal cell (BCC) and squamous cell cancers separately revealed very little difference in squamous cell cancer between treatment groups but a significant difference in new BCC (DFMO, 163 cancers; placebo, 243 cancers; expressed as event rate of 0.28 BCC/person/year versus 0.40 BCC/person/year, P = 0.03). Compliance with DFMO was >90% and it seemed to be well tolerated with evidence of mild ototoxicity as measured by serial audiometric examination when compared with placebo subjects. The analysis of normal skin biopsies revealed a significant (P < 0.05) decrease in 12-0-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced ODC activity (month 24, 36, and 48) and putrescine concentration (month 24 and 36 only) in DFMO subjects. Subjects with a history of skin cancer taking daily DFMO had an insignificant reduction (P = 0.069) in new NMSC that was predominantly due to a marked reduction in new BCC. Based on these data, the potential of DFMO, alone or in combination, to prevent skin cancers should be explored further.
Figures









Comment in
-
Targeting ornithine decarboxylase for the prevention of nonmelanoma skin cancer in humans.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2010 Jan;3(1):8-11. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-09-0248. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2010. PMID: 20051367 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:71–96. - PubMed
-
- Chen J, Fleisher AB, Jr, Smith ED, et al. Cost of non-melanoma skin cancer treatment in the United States. Dermatol Surg. 2001;27:1035–1038. - PubMed
-
- Lindelof B, Sigurgeirsson B, Gabel H, Stern RS. Incidence of skin cancer in 5356 patients following organ transplantation. Br J Dermatol. 2000;143(3):513–519. - PubMed
-
- Ramsay HM, Reece SM, Fryer AA, et al. Seven-year prospective study of non-melanoma skin cancer incidence in U.K. renal transplant recipients. Transplantation. 2007;84:437–439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

