Overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 in rat oral cancers and prevention of oral carcinogenesis in rats by selective and nonselective COX inhibitors
- PMID: 20051374
- PMCID: PMC2804934
- DOI: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-09-0151
Overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 in rat oral cancers and prevention of oral carcinogenesis in rats by selective and nonselective COX inhibitors
Abstract
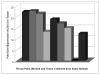
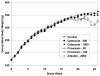
Oral squamous cell carcinomas induced in rats by 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide (NQO) show substantial overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) when compared with adjacent phenotypically normal oral tissues. By contrast, neither 5-lipoxygenase (LOX) nor 12-LOX is overexpressed in rat oral cancers. Two chemoprevention studies were done to test the resulting hypothesis that COX-2 is a useful target for oral cancer chemoprevention in the rat. In both studies, male F344 rats received drinking water exposure to NQO (20 ppm) for 10 weeks, followed by administration of chemopreventive agents from week 10 until study termination at week 26. In the first study, groups of rats were fed basal diet (control), or basal diet supplemented with the selective COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib (500 or 1,500 mg/kg diet), the nonselective COX inhibitor piroxicam (50 or 150 mg/kg diet), or the 5-LOX inhibitor zileuton (2,000 mg/kg diet). In the second study, rats were fed basal diet (control) or basal diet supplemented with nitric oxide-naproxen (180 or 90 mg/kg diet), a nonselective COX inhibitor that shows reduced gastrointestinal toxicity. When compared with dietary controls, celecoxib decreased oral cancer incidence, cancer invasion score, and cancer-related mortality. Piroxicam decreased cancer-related mortality and cancer invasion score, whereas nitric oxide-naproxen decreased oral cancer incidence and cancer invasion score. By contrast, zileuton showed no chemopreventive activity by any parameter assessed. These data show that both selective and nonselective inhibitors of COX-2 can prevent NQO-induced oral carcinogenesis in rats. The chemopreventive activity of COX inhibitors may be linked to overexpression of their enzymatic target in incipient oral neoplasms.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Overexpression of 5-lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase 2 in hamster and human oral cancer and chemopreventive effects of zileuton and celecoxib.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Mar 1;11(5):2089-96. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1684. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15756036
-
Dietary zinc modulation of COX-2 expression and lingual and esophageal carcinogenesis in rats.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005 Jan 5;97(1):40-50. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dji006. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005. PMID: 15632379
-
Chemopreventive properties of a selective inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor in colon carcinogenesis, administered alone or in combination with celecoxib, a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor.Cancer Res. 2002 Jan 1;62(1):165-70. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 11782374
-
Chemoprevention of colon cancer by specific cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, celecoxib, administered during different stages of carcinogenesis.Cancer Res. 2000 Jan 15;60(2):293-7. Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10667579
-
Increased expression of cyclooxygenase-2 protein in 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide-induced rat tongue carcinomas and chemopreventive efficacy of a specific inhibitor, nimesulide.Cancer Res. 2001 Feb 15;61(4):1451-6. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11245450
Cited by
-
Prevention of oral carcinogenesis in rats by Dracaena cinnabari resin extracts.Clin Oral Investig. 2019 May;23(5):2287-2301. doi: 10.1007/s00784-018-2685-6. Epub 2018 Oct 6. Clin Oral Investig. 2019. PMID: 30291495
-
Proapoptotic, anti-cell proliferative, anti-inflammatory and anti-angiogenic potential of carnosic acid during 7,12 dimethylbenz[a]anthracene-induced hamster buccal pouch carcinogenesis.Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2012 Oct 1;10(1):102-12. doi: 10.4314/ajtcam.v10i1.14. eCollection 2012. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2012. PMID: 24082331 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of lipocalins and pro-inflammatory chemokines and altered methylation of PTGS2 and APC2 in oral squamous cell carcinomas induced in rats by 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 30;10(1):e0116285. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116285. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25635769 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of Rat Oral Carcinogenesis by Agonists of Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor γ.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 30;10(10):e0141849. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141849. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26516762 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Pro-inflammatory and Anti-apoptotic Biomarkers during Experimental Oral Cancer Chemoprevention by Dietary Black Raspberries.Front Immunol. 2017 Oct 23;8:1325. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01325. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29109723 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gerson SJ. Oral cancer. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1990;1:153–66. - PubMed
-
- Shantz SP, Ostroff JS. Novel approaches to the prevention of head and neck cancer. Proc Soc Exptl Biol Med. 1998;216:275–82. - PubMed
-
- Boffetta P, Hecht S, Gray N, Gupta P, Straif K. Smokeless tobacco and cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2008;9:667–75. - PubMed
-
- Petersen PE. Oral cancer prevention and control—the approach of the World Health Organization. Oral Oncol. 2008;45:454–60. - PubMed
-
- Walker DM, Boey G, McDonald LA. The pathology of oral cancer. Pathology. 2003;35:376–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

