Pomegranate ellagitannin-derived compounds exhibit antiproliferative and antiaromatase activity in breast cancer cells in vitro
- PMID: 20051378
- PMCID: PMC2805471
- DOI: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-08-0225
Pomegranate ellagitannin-derived compounds exhibit antiproliferative and antiaromatase activity in breast cancer cells in vitro
Abstract
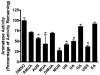
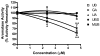
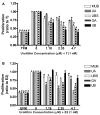
Estrogen stimulates the proliferation of breast cancer cells and the growth of estrogen-responsive tumors. The aromatase enzyme, which converts androgen to estrogen, plays a key role in breast carcinogenesis. The pomegranate fruit, a rich source of ellagitannins (ET), has attracted recent attention due to its anticancer and antiatherosclerotic properties. On consumption, pomegranate ETs hydrolyze, releasing ellagic acid, which is then converted to 3,8-dihydroxy-6H-dibenzo[b,d]pyran-6-one ("urolithin") derivatives by gut microflora. The purpose of this study was to investigate the antiaromatase activity and inhibition of testosterone-induced breast cancer cell proliferation by ET-derived compounds isolated from pomegranates. A panel of 10 ET-derived compounds including ellagic acid, gallagic acid, and urolithins A and B (and their acetylated, methylated, and sulfated analogues prepared in our laboratory) were examined for their ability to inhibit aromatase activity and testosterone-induced breast cancer cell proliferation. Using a microsomal aromatase assay, we screened the panel of ET-derived compounds and identified six with antiaromatase activity. Among these, urolithin B (UB) was shown to most effectively inhibit aromatase activity in a live cell assay. Kinetic analysis of UB showed mixed inhibition, suggesting more than one inhibitory mechanism. Proliferation assays also determined that UB significantly inhibited testosterone-induced MCF-7aro cell proliferation. The remaining test compounds also exhibited antiproliferative activity, but to a lesser degree than UB. These studies suggest that pomegranate ET-derived compounds have potential for the prevention of estrogen-responsive breast cancers.
Figures
References
-
- Fisher B, Costantino JP, Wickerham DL, et al. Tamoxifen for the prevention of breast cancer: current status of the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project P-1 study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97(22):1652–62. - PubMed
-
- Fisher B, Costantino JP, Wickerham DL, et al. Tamoxifen for prevention of breast cancer: report of the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project P-1 Study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998;90(18):1371–88. - PubMed
-
- Fisher B, Dignam J, Wolmark N, et al. Tamoxifen in treatment of intraductal breast cancer: National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project B-24 randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 1999;353(9169):1993–2000. - PubMed
-
- Morandi P, Rouzier R, Altundag K, et al. The role of aromatase inhibitors in the adjuvant treatment of breast carcinoma: the M. D. Anderson Cancer Center evidence-based approach. Cancer. 2004;101(7):1482–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

