The stress hormone corticosterone increases synaptic alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptors via serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase (SGK) regulation of the GDI-Rab4 complex
- PMID: 20051515
- PMCID: PMC2825404
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.050229
The stress hormone corticosterone increases synaptic alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptors via serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase (SGK) regulation of the GDI-Rab4 complex
Abstract
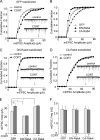
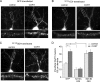
Corticosterone, the major stress hormone, plays an important role in regulating neuronal functions of the limbic system, although the cellular targets and molecular mechanisms of corticosteroid signaling are largely unknown. Here we show that a short treatment of corticosterone significantly increases alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPAR)-mediated synaptic transmission and AMPAR membrane trafficking in pyramidal neurons of prefrontal cortex, a key region involved in cognition and emotion. This enhancing effect of corticosterone is through a mechanism dependent on Rab4, the small GTPase-controlling receptor recycling between early endosome and plasma membrane. Guanosine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor (GDI), which regulates the cycle of Rab proteins between membrane and cytosol, forms an increased complex with Rab4 after corticosterone treatment. Corticosterone also triggers an increased GDI phosphorylation at Ser-213 by the serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase (SGK). Moreover, AMPAR synaptic currents and surface expression and their regulation by corticosterone are altered by mutating Ser-213 on GDI. These results suggest that corticosterone, via SGK phosphorylation of GDI at Ser-213, increases the formation of GDI-Rab4 complex, facilitating the functional cycle of Rab4 and Rab4-mediated recycling of AMPARs to the synaptic membrane. It provides a potential mechanism underlying the role of corticosteroid stress hormone in up-regulating excitatory synaptic efficacy in cortical neurons.
Figures



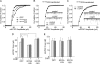
Similar articles
-
Spinal SGK1/GRASP-1/Rab4 is involved in complete Freund's adjuvant-induced inflammatory pain via regulating dorsal horn GluR1-containing AMPA receptor trafficking in rats.Pain. 2012 Dec;153(12):2380-2392. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2012.08.004. Epub 2012 Sep 11. Pain. 2012. PMID: 22980744
-
Mechanisms for acute stress-induced enhancement of glutamatergic transmission and working memory.Mol Psychiatry. 2011 Feb;16(2):156-70. doi: 10.1038/mp.2010.50. Epub 2010 May 11. Mol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 20458323 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of AMPA receptor trafficking and function by glycogen synthase kinase 3.J Biol Chem. 2010 Aug 20;285(34):26369-76. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.121376. Epub 2010 Jun 28. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20584904 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of neuronal PKA signaling through AKAP targeting dynamics.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;85(7):627-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.01.010. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16504338 Review.
-
Palmitoylation-mediated synaptic regulation of AMPA receptor trafficking and function.Arch Pharm Res. 2019 May;42(5):426-435. doi: 10.1007/s12272-019-01134-z. Epub 2019 Mar 5. Arch Pharm Res. 2019. PMID: 30838509 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular control of Rab activity by GEFs, GAPs and GDI.Small GTPases. 2018 Mar 4;9(1-2):5-21. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1276999. Epub 2017 Feb 1. Small GTPases. 2018. PMID: 28055292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucocorticoid and β-adrenergic regulation of hippocampal dendritic spines.J Neuroendocrinol. 2020 Jan;32(1):e12811. doi: 10.1111/jne.12811. Epub 2019 Dec 5. J Neuroendocrinol. 2020. PMID: 31715030 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of excitatory synapses and fearful memories by stress hormones.Front Behav Neurosci. 2011 Oct 11;5:62. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2011.00062. eCollection 2011. Front Behav Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22013419 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of SGK1 in the regulation of neuronal function.J Physiol. 2010 Sep 15;588(Pt 18):3349-54. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.190926. Epub 2010 Jun 7. J Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20530112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endogenous retroviral pathogenesis in lupus.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010 Sep;22(5):483-92. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e32833c6297. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010. PMID: 20644481 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McEwen B. S. (1999) Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 22, 105–122 - PubMed
-
- McEwen B. S. (2007) Physiol. Rev. 87, 873–904 - PubMed
-
- de Kloet E. R., Joëls M., Holsboer F. (2005) Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 6, 463–475 - PubMed
-
- Joëls M., Krugers H. J., Lucassen P. J., Karst H. (2009) Brain Res. 1293, 91–100 - PubMed
-
- Karst H., Joëls M. (2005) J. Neurophysiol. 94, 3479–3486 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

