Impaired alpha(IIb)beta(3) integrin activation and shear-dependent thrombus formation in mice lacking phospholipase D1
- PMID: 20051593
- PMCID: PMC3701458
- DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.2000551
Impaired alpha(IIb)beta(3) integrin activation and shear-dependent thrombus formation in mice lacking phospholipase D1
Abstract
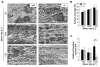
Platelet aggregation is essential for hemostasis but can also cause myocardial infarction and stroke. A key but poorly understood step in platelet activation is the shift of the principal adhesive receptor, alpha(IIb)beta(3) integrin, from a low- to high-affinity state for its ligands, a process that enables adhesion and aggregation. In response to stimulation of heterotrimeric guanosine triphosphate-binding protein or immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif-coupled receptors, phospholipases cleave membrane phospholipids to generate lipid and soluble second messengers. An essential role in platelet activation has been established for phospholipase C (PLC) but not for PLD and its product phosphatidic acid. Here, we report that platelets from Pld1(-/-) mice displayed impaired alpha(IIb)beta(3) integrin activation in response to major agonists and defective glycoprotein Ib-dependent aggregate formation under high shear conditions. These defects resulted in protection from thrombosis and ischemic brain infarction without affecting tail bleeding times. These results indicate that PLD1 may be a critical regulator of platelet activity in the setting of ischemic cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events.
Figures

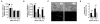


References
-
- Ruggeri ZM. Platelets in atherothrombosis. Nat. Med. 2002;8:1227–1234. - PubMed
-
- Bhatt DL, Topol EJ. Scientific and therapeutic advances in antiplatelet therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003;2:15–28. - PubMed
-
- Stoll G, Kleinschnitz C, Nieswandt B. Molecular mechanisms of thrombus formation in ischemic stroke: novel insights and targets for treatment. Blood. 2008;112:3555–3562. - PubMed
-
- Savage B, mus-Jacobs F, Ruggeri ZM. Specific synergy of multiple substrate-receptor interactions in platelet thrombus formation under flow. Cell. 1998;94:657–666. - PubMed
-
- Ozaki Y, Asazuma N, Suzuki-Inoue K, Berndt C. Platelet GPIb-IX-V-dependent signaling. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005;3:1745–1751. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

