Enabling stem cell therapies through synthetic stem cell-niche engineering
- PMID: 20051637
- PMCID: PMC2798701
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI41158
Enabling stem cell therapies through synthetic stem cell-niche engineering
Abstract
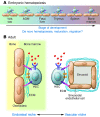
Enabling stem cell-targeted therapies requires an understanding of how to create local microenvironments (niches) that stimulate endogenous stem cells or serve as a platform to receive and guide the integration of transplanted stem cells and their derivatives. In vivo, the stem cell niche is a complex and dynamic unit. Although components of the in vivo niche continue to be described for many stem cell systems, how these components interact to modulate stem cell fate is only beginning to be understood. Using the HSC niche as a model, we discuss here microscale engineering strategies capable of systematically examining and reconstructing individual niche components. Synthetic stem cell-niche engineering may form a new foundation for regenerative therapies.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

