EWS-Oct-4B, an alternative EWS-Oct-4 fusion gene, is a potent oncogene linked to human epithelial tumours
- PMID: 20051954
- PMCID: PMC2816667
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605516
EWS-Oct-4B, an alternative EWS-Oct-4 fusion gene, is a potent oncogene linked to human epithelial tumours
Abstract
Background: Characterisation of EWS-Oct-4 translocation fusion product in bone and soft-tissue tumours revealed a chimeric gene resulting from an in-frame fusion between EWS (Ewing's sarcoma gene) exons 1-6 and Oct-4 exons 1-4. Recently, an alternative form of the fusion protein between the EWS and Oct-4 genes, named EWS-Oct-4B, was reported in two types of epithelial tumours, a hidradenoma of the skin and a mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the salivary glands. As the N-terminal and POU domains of the EWS-Oct-4 and EWS-Oct-4B proteins are not structurally identical, we decided to investigate the functional consequences of the EWS-Oct-4B fusion.
Methods: In this report, we have characterised the EWS-Oct-4B fusion protein. To investigate how the EWS-Oct-4B protein contributes to tumourigenesis in human cancers, we analysed its DNA-binding activity, subcellular localisation, transcriptional activation behaviour, and oncogenic properties.
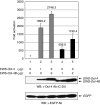
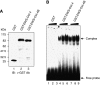
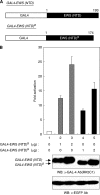
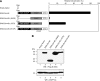
Results: We found that this new chimeric gene encodes a nuclear protein that binds DNA with the same sequence specificity as the parental Oct-4 protein or the fusion EWS-Oct-4 protein. We show that the nuclear localisation signal of EWS-Oct-4B is dependent on the POU DNA-binding domain, and we identified a cluster of basic amino acids, (269)RKRKR(273), in the POU domain that specifically mediates the nuclear localisation of EWS-Oct-4B. Comparison of the properties of EWS-Oct-4B and EWS-Oct-4 indicated that EWS-Oct-4B is a less-potent transcriptional activator of a reporter construct carrying the Oct-4-binding sites. Deletion analysis of the functional domains of EWS-Oct-4B revealed that the EWS N-terminal domain (NTD)(B), POU, and C-terminal domain (CTD) are necessary for its full transactivation potential. Despite its reduced activity as a transcriptional activator, EWS-Oct-4B regulated the expression of fgf-4 (fibroblast growth factor-4) and nanog, which are potent mitogens, as well as of Oct-4 downstream target genes, the promoters of which contain potential Oct-4-binding sites. Finally, ectopic expression of EWS-Oct-4B in Oct-4-null ZHBTc4 ES cells resulted in increased tumourigenic growth potential in nude mice.
Conclusion: These results suggest that the oncogenic effect of the t(6;22) translocation is due to the EWS-Oct-4B chimeric protein, and that alternative fusion of the EWS amino terminal domain to the Oct-4 DNA-binding domain produces another transforming chimeric product in human epithelial tumours.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The EWS-Oct-4 fusion gene encodes a transforming gene.Biochem J. 2007 Sep 15;406(3):519-26. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070243. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17564582 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role of the fibroblast growth factor signalling pathway in Ewing's sarcoma octamer-binding transcription factor 4-mediated cell proliferation and tumorigenesis.FEBS J. 2019 Nov;286(22):4443-4472. doi: 10.1111/febs.14946. Epub 2019 Jun 12. FEBS J. 2019. PMID: 31155838
-
Mutation in the DNA-binding domain of the EWS-Oct-4 oncogene results in dominant negative activity that interferes with EWS-Oct-4-mediated transactivation.Int J Cancer. 2009 May 15;124(10):2312-22. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24228. Int J Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19170206
-
Oncogenic partnerships: EWS-FLI1 protein interactions initiate key pathways of Ewing's sarcoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Aug 15;16(16):4077-83. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2261. Epub 2010 Jun 14. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20547696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EWS-FLI1 in Ewing's sarcoma: real targets and collateral damage.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006;587:41-52. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4020-5133-3_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2006. PMID: 17163154 Review.
Cited by
-
Visualization of early prostatic adenocarcinoma as a stem cell disease.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 15;7(46):76159-76168. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12709. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27764770 Free PMC article.
-
Psoriasis regression analysis of MHC loci identifies shared genetic variants with vitiligo.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e23089. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023089. Epub 2011 Nov 18. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22125590 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms and pathobiology of oncogenic fusion transcripts in epithelial tumors.Oncotarget. 2019 Mar 12;10(21):2095-2111. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26777. eCollection 2019 Mar 12. Oncotarget. 2019. PMID: 31007851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The self-renewal function of Oct-4 can be replaced by the EWS-Oct-4 fusion protein in embryonic stem cells.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025 Apr 18;82(1):166. doi: 10.1007/s00018-025-05701-0. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40251420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aasen T, Raya A, Barrero MJ, Garreta E, Consiglio A, Gonzalez F, Vassena R, Bilic J, Pekarik V, Tiscornia G, Edel M, Boue S, Belmonte JC (2008) Efficient and rapid generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from human keratinocytes. Nat Biotechnol 26: 1276–1284 - PubMed
-
- Breeuwer M, Goldfarb DS (1990) Facilitated nuclear transport of histone H1 and other small nucleophilic proteins. Cell 60: 999–1008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

