MicroRNA assassins: factors that regulate the disappearance of miRNAs
- PMID: 20051982
- PMCID: PMC6417416
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1762
MicroRNA assassins: factors that regulate the disappearance of miRNAs
Abstract
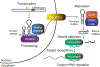
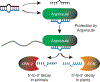
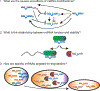
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) control essential gene regulatory pathways in plants and animals. Serving as guides in silencing complexes, miRNAs direct Argonaute proteins to specific target messenger RNAs to repress protein expression. The mature, 22-nucleotide (nt) miRNA is the product of multiple processing steps, and recent studies have uncovered factors that directly control the stability of the functional RNA form. Although alteration of miRNA levels has been linked to numerous disease states, the mechanisms responsible for stabilized or reduced miRNA expression have been largely elusive. The discovery of specific cis-acting modifications and trans-acting proteins that affect miRNA half-life reveals new elements that contribute to the homeostasis of these vital regulatory molecules.
Figures
References
-
- Hebert SS & De Strooper B Alterations of the microRNA network cause neurodegenerative disease. Trends Neurosci. 32, 199–206 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Latronico MV & Condorelli G MicroRNAs and cardiac pathology. Nat. Rev. Cardiol 6, 419–429 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Negrini M, Nicoloso MS & Calin GA MicroRNAs and cancer—new paradigms in molecular oncology. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol 21, 470–479 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Chuck G, Candela H & Hake S Big impacts by small RNAs in plant development. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol 12, 81–86 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

