The liver plays a major role in clearance and destruction of blood trypomastigotes in Trypanosoma cruzi chronically infected mice
- PMID: 20052269
- PMCID: PMC2793026
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000578
The liver plays a major role in clearance and destruction of blood trypomastigotes in Trypanosoma cruzi chronically infected mice
Abstract
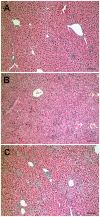
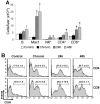
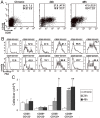
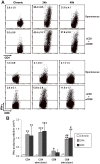
Intravenous challenge with Trypanosoma cruzi can be used to investigate the process and consequences of blood parasite clearance in experimental Chagas disease. One hour after intravenous challenge of chronically infected mice with 5x10(6) trypomastigotes, the liver constituted a major site of parasite accumulation, as revealed by PCR. Intact parasites and/or parasite remnants were visualized at this time point scattered in the liver parenchyma. Moreover, at this time, many of liver-cleared parasites were viable, as estimated by the frequency of positive cultures, which considerably diminished after 48 h. Following clearance, the number of infiltrating cells in the hepatic tissue notably increased: initially (at 24 h) as diffuse infiltrates affecting the whole parenchyma, and at 48 h, in the form of large focal infiltrates in both the parenchyma and perivascular spaces. Phenotypic characterization of liver-infiltrating cells 24 h after challenge revealed an increase in Mac1(+), CD8(+) and CD4(+) cells, followed by natural killer (NK) cells. As evidence that liver-infiltrating CD4(+) and CD8(+) cells were activated, increased frequencies of CD69(+)CD8(+), CD69(+)CD4(+) and CD25(+)CD122(+)CD4(+) cells were observed at 24 and 48 h after challenge, and of CD25(-)CD122(+)CD4(+) cells at 48 h. The major role of CD4(+) cells in liver protection was suggested by data showing a very high frequency of interferon (IFN)-gamma-producing CD4(+) cells 24 h after challenge. In contrast, liver CD8(+) cells produced little IFN-gamma, even though they showed an enhanced potential for secreting this cytokine, as revealed by in vitro T cell receptor (TCR) stimulation. Confirming the effectiveness of the liver immune response in blood parasite control during the chronic phase of infection, no live parasites were detected in this organ 7 days after challenge.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
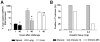

References
-
- Avila HA, Sigman DS, Cohen LM, Millikan RC, Simpson L. Polymerase chain reaction amplification of Trypanosoma cruzi kinetoplast minicircle DNA isolated from whole blood lysates: diagnosis of chronic Chagas' disease. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991;48:211–221. - PubMed
-
- Marinho CR, Bastos KR, Sardinha LR, Grisotto MG, Lima MR, et al. Challenge of Trypanosoma cruzi chronically infected mice with trypomastigotes activates the immune system and reduces subpatent parasitemia levels. J Parasitol. 2004;90:516–523. - PubMed
-
- Russo M, Starobinas N, Marcondes MC, Minoprio P, Honteyberie-Joskowicz M. The influence of T cell subsets on Trypanosoma cruzi multiplication in different organs. Immunol Lett. 1996;49:163–168. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

