CRF1-R activation of the dynorphin/kappa opioid system in the mouse basolateral amygdala mediates anxiety-like behavior
- PMID: 20052275
- PMCID: PMC2795205
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008528
CRF1-R activation of the dynorphin/kappa opioid system in the mouse basolateral amygdala mediates anxiety-like behavior
Abstract
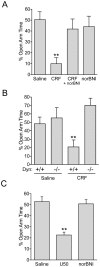
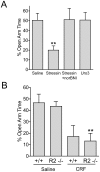
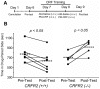
Stress is a complex human experience and having both rewarding and aversive motivational properties. The adverse effects of stress are well documented, yet many of underlying mechanisms remain unclear and controversial. Here we report that the anxiogenic properties of stress are encoded by the endogenous opioid peptide dynorphin acting in the basolateral amygdala. Using pharmacological and genetic approaches, we found that the anxiogenic-like effects of Corticotropin Releasing Factor (CRF) were triggered by CRF(1)-R activation of the dynorphin/kappa opioid receptor (KOR) system. Central CRF administration significantly reduced the percent open-arm time in the elevated plus maze (EPM). The reduction in open-arm time was blocked by pretreatment with the KOR antagonist norbinaltorphimine (norBNI), and was not evident in mice lacking the endogenous KOR ligand dynorphin. The CRF(1)-R agonist stressin 1 also significantly reduced open-arm time in the EPM, and this decrease was blocked by norBNI. In contrast, the selective CRF(2)-R agonist urocortin III did not affect open arm time, and mice lacking CRF(2)-R still showed an increase in anxiety-like behavior in response to CRF injection. However, CRF(2)-R knockout animals did not develop CRF conditioned place aversion, suggesting that CRF(1)-R activation may mediate anxiety and CRF(2)-R may encode aversion. Using a phosphoselective antibody (KORp) to identify sites of dynorphin action, we found that CRF increased KORp-immunoreactivity in the basolateral amygdala (BLA) of wildtype, but not in mice pretreated with the selective CRF(1)-R antagonist, antalarmin. Consistent with the concept that acute stress or CRF injection-induced anxiety was mediated by dynorphin release in the BLA, local injection of norBNI blocked the stress or CRF-induced increase in anxiety-like behavior; whereas norBNI injection in a nearby thalamic nucleus did not. The intersection of stress-induced CRF and the dynorphin/KOR system in the BLA was surprising, and these results suggest that CRF and dynorphin/KOR systems may coordinate stress-induced anxiety behaviors and aversive behaviors via different mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Müller MB, Zimmermann S, Sillaber I, Hagemeyer TP, Deussing JM, et al. Limbic corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor1 mediates anxiety-related behavior and hormonal adaptation to stress. Nat Neurosci. 2003;10:1100–1107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

