Serum cystatin C is a potential endogenous marker for the estimation of renal function in male gout patients with renal impairment
- PMID: 20052346
- PMCID: PMC2800003
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.1.42
Serum cystatin C is a potential endogenous marker for the estimation of renal function in male gout patients with renal impairment
Abstract
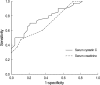
Serum creatinine level is the most commonly used indices for assessment of glomerular filtration rate (GFR), even though these indices have been shown to have some limitations in clinical practice. We investigated the diagnostic efficacy of serum cystatin C compared to that of serum creatinine levels and identified the relating factors associated with changes in serum cystatin C levels in gout patients with renal impairment. A total of 68 gouty patients with renal impairment were enrolled in this study. Diagnostic efficacy of serum cystatin C levels was evaluated through non-parametric receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis. The risk factors for changes in serum cystatin C levels were confirmed using multivariate regression analysis. With 24-hr urine creatinine clearance (Ccr) as the reference for GFR, 1/cystatin C (r=0.702, P<0.001) showed a significantly higher correlation with Ccr than 1/creatinine (r=0.665, P<0.001). Multivariate correlation analysis demonstrated that the clinical parameters for increased serum cystatin C are a higher stage of chronic kidney disease, older age, use of allopurinol, and lower high density lipoprotein-cholesterol. The area under the curve (AUC) at ROC plots identified that of serum cystatin C was significantly greater than that of serum creatinine (AUC 0.804 of cystatin C and AUC 0.745 of creatinine). The study suggests that serum cystatin C is a reliable endogenous marker for the assessment of renal function or GFR in gout patients with renal impairment.
Keywords: Creatinine; Cystatin C; Glomerular Filtration Rate; Gout; Kidney Failure.
Figures
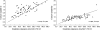
Similar articles
-
Serum cystatin C concentration compared with other markers of glomerular filtration rate in the old old.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002 Jul;50(7):1278-82. doi: 10.1046/j.1532-5415.2002.50317.x. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002. PMID: 12133025
-
Correlation of Serum Cystatin C with Renal Function in Gout Patients with Renal Injury.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2021 Sep;41(9):329-335. doi: 10.1089/jir.2021.0034. Epub 2021 Aug 25. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2021. PMID: 34435875
-
Role of Cystatin C and glomerular filtration rate in diagnosis of kidney impairment in hepatic cirrhosis patients.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 May;96(20):e6949. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006949. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28514315 Free PMC article.
-
Estimating renal function in children: a new GFR-model based on serum cystatin C and body cell mass.Dan Med J. 2012 Jul;59(7):B4486. Dan Med J. 2012. PMID: 22759853 Review.
-
The value of serum cystatin C in early evaluation of renal insufficiency in patients undergoing chemotherapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2019 Mar;83(3):561-571. doi: 10.1007/s00280-018-3762-x. Epub 2019 Jan 4. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30610366
Cited by
-
Potential of IL-33 for Preventing the Kidney Injury via Regulating the Lipid Metabolism in Gout Patients.J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016:1028401. doi: 10.1155/2016/1028401. Epub 2016 Aug 7. J Diabetes Res. 2016. PMID: 27579324 Free PMC article.
-
Cystatin C as an early biomarker of nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes.J Korean Med Sci. 2011 Feb;26(2):258-63. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.2.258. Epub 2011 Jan 24. J Korean Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 21286018 Free PMC article.
-
Indicators of Male Gout Patients' Comorbidities with the Theory on Traditional Chinese Medicine.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Dec 4;2018:9679213. doi: 10.1155/2018/9679213. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 30622620 Free PMC article.
-
Reference intervals for serum cystatin C and factors influencing cystatin C levels other than renal function in the elderly.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 21;9(1):e86066. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086066. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24465871 Free PMC article.
-
Estimated glomerular filtration rate in clinical practice: Consensus positioning of the Brazilian Society of Nephrology (SBN) and Brazilian Society of Clinical Pathology and Laboratory Medicine (SBPC/ML).J Bras Nefrol. 2024 Apr 5;46(3):e20230193. doi: 10.1590/2175-8239-JBN-2023-0193en. eCollection 2024. J Bras Nefrol. 2024. PMID: 38591823 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Herget-Rosenthal S, Bökenkamp A, Hofmann W. How to estimate GFR-serum creatinine, serum cystatin C or equations? Clin Biochem. 2007;40:153–161. - PubMed
-
- Perrone RD, Steinman TI, Beck GJ, Skibinski CI, Royal HD, Lawlor M, Hunsicker LG. Utility of radioisotopic filtration markers in chronic renal insufficiency: simultaneous comparison of 125I-iothalamate, 169Yb-DTPA, 99mTc-DTPA, and inulin. The Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study. Am J Kidney Dis. 1990;16:224–235. - PubMed
-
- Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB, Greene T, Rogers N, Roth D. A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group. Ann Intern Med. 1999;130:461–470. - PubMed
-
- Cockcroft DW, Gault MH. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron. 1976;16:31–41. - PubMed
-
- Grubb A, Simonsen O, Sturfelt G, Truedsson L, Thysell H. Serum concentration of cystatin C, factor D and beta 2-microglobulin as a measure of glomerular filtration rate. Acta Med Scand. 1985;218:499–503. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

