The anti-inflammatory effects of ulinastatin in trauma patients with hemorrhagic shock
- PMID: 20052358
- PMCID: PMC2800012
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.1.128
The anti-inflammatory effects of ulinastatin in trauma patients with hemorrhagic shock
Abstract
We investigated the use of ulinastatin in association with the suppression of polymorphonuclear leukocyte elastase (PMNE), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin 6 (IL-6), and its effects on the prognosis of patients with traumatic hemorrhagic shock. Nineteen patients who visited the emergency department for traumatic hemorrhagic shock were enrolled. Eleven patients were randomly selected to receive a total of 300,000 IU of ulinastatin. Measurements of serum PMNE, TNF-alpha and IL-6 were taken before ulinastatin treatment at 24 hr, two days, three days, and seven days after admission. We compared the Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome scores, Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome scores and Acute Physiology, age, Chronic Health Evaluation III scores of the control and ulinastatin groups. There were no significant differences in baseline values, laboratory data, treatment or mortality between the two groups. The serum PMNE levels in the ulinastatin group were lower than in the control group on the second hospitalized day. Serum TNF-alpha and IL-6 levels in the ulinastatin group decreased 24 hr after admission but had no significance. It is suggested that ulinastatin treatment could decrease the serum PMNE levels in trauma patients with hemorrhagic shock at 48 hr after treatment.
Keywords: Interleukin-6; Leukocyte Elastase; Shock, Hemorrhagic; Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha; Ulinastatin.
Figures

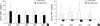
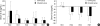

Similar articles
-
Does intraoperative ulinastatin improve postoperative clinical outcomes in patients undergoing cardiac surgery: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:630835. doi: 10.1155/2014/630835. Epub 2014 Mar 9. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24734237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Clinical study on effects of ulinastatin on patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome].Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2005 Apr;17(4):228-30. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2005. PMID: 15836828 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
[Mechanism of ulinastatin in reducing lung inflammatory injury in rats with hemorrhagic shock].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2019 Oct 30;39(10):1232-1238. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2019.10.16. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2019. PMID: 31801723 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Effects of high-dose ulinastatin on inflammatory response and pulmonary function in patients with type-A aortic dissection after cardiopulmonary bypass under deep hypothermic circulatory arrest.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2013 Jun;27(3):479-84. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2012.11.001. Epub 2013 Mar 30. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2013. PMID: 23545347 Clinical Trial.
-
Ulinastatin - a newer potential therapeutic option for multiple organ dysfunction syndrome.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2016 Mar;27(2):91-9. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2015-0003. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26565549 Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of urinary trypsin inhibitor against neuropathic pain in rat models.Korean J Pain. 2013 Oct;26(4):356-60. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2013.26.4.356. Epub 2013 Oct 2. Korean J Pain. 2013. PMID: 24156001 Free PMC article.
-
Does intraoperative ulinastatin improve postoperative clinical outcomes in patients undergoing cardiac surgery: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:630835. doi: 10.1155/2014/630835. Epub 2014 Mar 9. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24734237 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ulinastatin alleviates neuroinflammation but fails to improve cognitive function in aged rats following partial hepatectomy.Neurochem Res. 2013 May;38(5):1070-7. doi: 10.1007/s11064-013-1018-z. Epub 2013 Mar 19. Neurochem Res. 2013. PMID: 23508312
-
Ulinastatin Protects against Acute Kidney Injury in Infant Piglets Model Undergoing Surgery on Hypothermic Low-Flow Cardiopulmonary Bypass.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 14;10(12):e0144516. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144516. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26656098 Free PMC article.
-
Early pulmonary immune hyporesponsiveness is associated with mortality after burn and smoke inhalation injury.J Burn Care Res. 2012 Jan-Feb;33(1):26-35. doi: 10.1097/BCR.0b013e318234d903. J Burn Care Res. 2012. PMID: 21979852 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maitra SR, Gestring M, el-Maghrabi MR. Alternations in hepatic 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase and glucose-6-phosphatase gene expression after hemorrhagic hypotension and resuscitation. Shock. 1997;8:385–388. - PubMed
-
- Lee CC, Marill KA, Carter WA, Crupi RS. A current concept of trauma-induced multiorgan failure. Ann Emerg Med. 2001;38:170–176. - PubMed
-
- Riedemann NC, Neff TA, Guo RF, Bernacki KD, Laudes IJ, Sarma JV, Lambris JD, Ward PA. Protective effects of IL-6 blockade in sepsis are linked to reduced c5a receptor expression. J Immunol. 2003;170:503–507. - PubMed
-
- Nishiyama T, Hanaoka K. Do the effects of a protease inhibitor, ulinastatin, on elastase release by blood transfusion depend on interleukin 6? Crit Care Med. 2001;29:2106–2110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

