Crusted (Norwegian) scabies following systemic and topical corticosteroid therapy
- PMID: 20052371
- PMCID: PMC2800004
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.1.188
Crusted (Norwegian) scabies following systemic and topical corticosteroid therapy
Abstract
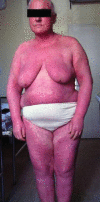
It is a case study of a 62-yr-old female with crusted (Norwegian) scabies, which appeared during her treatment with systemic and topical corticosteroid therapy, under the diagnosis of erythroderma. In the same time, the patient had been suffered from hypothyoidism, and her skin changes were misdiagnosed, because it was thought that they are associated with her endocrine disorder. Suddenly, beside the erythema, her skin became hyperkeratotic, with widespread scaling over the trunk and limbs, and crusted lesions appeared on her scalp and ears. The microscopic examination of the skin scales with potassium hydroxide demonstrated numerous scabies mites and eggs. Repeated topical treatments with lindan, benzoyl benzoat and 10% precipitated sulphur ointment led to the complete resolution of her skin condition.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Sarcoptes Scabiei; Therapy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Diagnostic dilemma: crusted scabies superimposed on psoriatic erythroderma in a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome.Skinmed. 2007 May-Jun;6(3):142-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-9740.2007.05723.x. Skinmed. 2007. PMID: 17483659
-
Unusual presentation of crusted scabies with osteolysis in immunocompetent.Australas J Dermatol. 2021 Nov;62(4):e563-e567. doi: 10.1111/ajd.13726. Epub 2021 Sep 27. Australas J Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 34570367
-
Crusted Norwegian scabies in an adult with Langerhans cell histiocytosis: mishaps leading to systemic chemotherapy.Arch Dermatol. 2007 May;143(5):626-8. doi: 10.1001/archderm.143.5.626. Arch Dermatol. 2007. PMID: 17515513
-
Crusted scabies associated with systemic lupus erythematosus: response to benzyl benzoate therapy.J Med Assoc Thai. 1996 Jan;79(1):65-8. J Med Assoc Thai. 1996. PMID: 8867406 Review.
-
Management of scabies.Singapore Med J. 2019 Jun;60(6):281-285. doi: 10.11622/smedj.2019058. Singapore Med J. 2019. PMID: 31243462 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Norwegian Scabies in a 70-Year-Old Renal Transplant Recipient: A Case Report.Iran J Parasitol. 2023 Apr-Jun;18(2):257-261. doi: 10.18502/ijpa.v18i2.13193. Iran J Parasitol. 2023. PMID: 37583641 Free PMC article.
-
Crusted scabies due to indiscriminate use of glucocorticoid therapy in infant.An Bras Dermatol. 2017 May-Jun;92(3):383-385. doi: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20174433. An Bras Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 29186253 Free PMC article.
-
Previous Long-term Care Facility Admission as a Risk Factor for Scabies in a Medical Facility.J Korean Med Sci. 2021 Dec 20;36(49):e337. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e337. J Korean Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34931498 Free PMC article.
-
An elderly long-term care resident with crusted scabies.Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2015 Jan-Feb;26(1):39-40. doi: 10.1155/2015/540156. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25798153 Free PMC article.
-
Severe Scabies: A French Multi-centre Study Involving 95 Patients with Crusted and Profuse Disease and Review of the Literature.Acta Derm Venereol. 2023 Mar 2;103:adv00878. doi: 10.2340/actadv.v103.5351. Acta Derm Venereol. 2023. PMID: 36861856 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Landwehr D, Keita SM, Ponnighaus JM, Tounkara C. Epidemiologic aspects of scabies in Mali, Malawi and Cambodia. Int J Dermatol. 1998;37:588–590. - PubMed
-
- Cox NH, Paterson WD. Epidemiology of scabies: the new epidemic. Lancet. 1991;337:1547–1548. - PubMed
-
- Burns DA. Diseases caused by arthropods and other noxious animals. In: Champion RH, Burton JL, Burns DA, Breathnach SM, editors. Rook, Wilkinson Textbook of Dermatology. 6th ed. Oxford: Blackwell Science; 1998. pp. 1423–1482.
-
- Portu JJ, Santamaria MJ, Zubero Z, Almeida-Liamas M, Etxebarria San Sebastian MA, Gutierrez AR. Atypical scabies in HIV positive patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1996;34:915–917. - PubMed
-
- Suzumiya J, Sumiyoshi A, Kuroki Y, Inoue S. Crusted (Norwegian) scabies with adult T-cell leukemia. Arch Dermatol. 1985;121:903–904. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

