Composition and morphology of nanocrystals in urines of lithogenic patients and healthy persons
- PMID: 20052395
- PMCID: PMC2801016
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/925297
Composition and morphology of nanocrystals in urines of lithogenic patients and healthy persons
Abstract
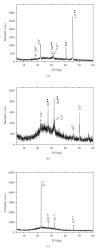
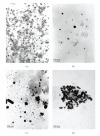
The composition and morphology of nanocrystals in urines of healthy persons and lithogenic patients were comparatively investigated by means of X-ray diffraction (XRD) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). It was shown that the main composition of urinary nanocrystals in healthy persons were calcium oxalate dihydrate (COD), uric acid, and ammonium magnesium phosphate (struvite). However, the main compositions of urinary nanocrystals in lithogenic patients were struvite, beta-tricalcium phosphate, uric acid, COD, and calcium oxalate monohydrate (COM). According to the XRD data, the size of nanocrystals was calculated to be 23 approximately 72 nm in healthy urine and 12 approximately 118 nm in lithogenic urine by Scherer formula. TEM results showed that the nanocrystals in healthy urine were dispersive and uniform with a mean size of about 38 nm. In contrast, the nanocrystals in lithogenic urine were much aggregated with a mean size of about 55 nm. The results in this work indicated that the urinary stone formation may be prevented by diminishing the aggregation and the size differentiation of urinary nanocrystals by physical or chemical methods.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Morphology, particle size distribution, aggregation, and crystal phase of nanocrystallites in the urine of healthy persons and lithogenic patients.IEEE Trans Nanobioscience. 2010 Jun;9(2):156-63. doi: 10.1109/TNB.2010.2045510. Epub 2010 Apr 26. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience. 2010. PMID: 20423812
-
[Study on nano- and microcrystallites in the urines of calcium oxalate stone formers].Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi. 2010 Jul;30(7):1913-7. Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi. 2010. PMID: 20827998 Chinese.
-
Lithogenic activity and clinical relevance of lipids extracted from urines and stones of nephrolithiasis patients.Urol Res. 2011 Feb;39(1):9-19. doi: 10.1007/s00240-010-0281-6. Epub 2010 May 28. Urol Res. 2011. PMID: 20509023
-
[May renal lithiasis be really prevented? New trends and therapeutic tools.].Arch Esp Urol. 2017 Jan;70(1):91-102. Arch Esp Urol. 2017. PMID: 28221144 Review. Spanish.
-
Renal lithiasis and nutrition.Nutr J. 2006 Sep 6;5:23. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-5-23. Nutr J. 2006. PMID: 16956397 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tsujihata M. Mechanism of calcium oxalate renal stone formation and renal tubular cell injury. International Journal of Urology. 2008;15(2):115–120. - PubMed
-
- Felix G, Antonia CB, Margarita R, Vicente M, Antonio C. Simple classification of renal calculi closely related to their micromorphology and etiology. Clinica Chimica Acta. 2002;322:29–36. - PubMed
-
- Ochmanski W, Kmiecik J, SuLowicz W. Analysis of chemical composition of urinary stones. International Urology and Nephrology. 1999;31(6):743–750.
-
- Kofina AN, Koutsoukos PG. Spontaneous precipitation of struvite from synthetic wastewater solutions. Crystal Growth and Design. 2005;5(2):489–496.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

