Double positive CD4CD8 alphabeta T cells: a new tumor-reactive population in human melanomas
- PMID: 20052413
- PMCID: PMC2797605
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008437
Double positive CD4CD8 alphabeta T cells: a new tumor-reactive population in human melanomas
Abstract
Background: Double positive (DP) CD4CD8 Talphabeta cells have been reported in normal individuals as well as in different pathological conditions including inflammatory diseases, viral infections and cancer, but their function remains to be elucidated. We recently reported the increased frequency of DP Talphabeta cells in human breast pleural effusions. This manuscript addresses the question of the existence and above all the role of this non-conventional DP sub-population among tumor associated lymphocytes in melanomas.
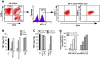
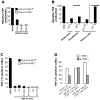
Methodology/principal findings: We analyzed the intratumoral cell infiltrate in solid metastasis (n = 6) and tumor invaded lymph nodes (n = 26) samples from melanomas patients by multiparametric cytometry. Here we documented for the first time significant increased frequency of DP T cells in about 60% of melanoma tumors compared to blood samples. Interestingly, a high proportion of these cells produced TNF-alpha in response to autologous melanoma cell lines. Besides, they are characterized by a unique cytokine profile corresponding to higher secretion of IL-13, IL-4 and IL-5 than simple positive T cells. In deep analysis, we derived a representative tumor-reactive DP T cell clone from a melanoma patient's invaded lymph node. This clone was restricted by HLA-A*2402 and recognized both autologous and allogeneic tumor cells of various origins as well as normal cells, suggesting that the target antigen was a ubiquitous self antigen. However, this DP T cell clone failed to kill HLA-A*2402 EBV-transformed B cells, probably due to the constitutive expression of immunoproteasome by these cells.
Conclusions/significance: In conclusion, we can postulate that, according to their broad tumor reactivity and to their original cytokine profile, the tumor associated DP T cells could participate in immune responses to tumors in vivo. Therefore, the presence of these cells and their role will be crucial to address in cancer patients, especially in the context of immunotherapies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Dunn GP, Old LJ, Schreiber RD. The immunobiology of cancer immunosurveillance and immunoediting. Immunity. 2004;21(2):137–148. - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg SA. Progress in human tumour immunology and immunotherapy. Nature. 2001;411(6835):380–384. - PubMed
-
- Appay V, Douek DC, Price DA. CD8+ T cell efficacy in vaccination and disease. Nat Med. 2008;14(6):623–628. - PubMed
-
- Khammari A, Labarriere N, Vignard V, Nguyen JM, Pandolfino MC, et al. Treatment of Metastatic Melanoma with Autologous Melan-A/Mart-1-Specific Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Clones. J Invest Dermatol 2009 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

