The anti-inflammatory effects of adiponectin are mediated via a heme oxygenase-1-dependent pathway in rat Kupffer cells
- PMID: 20052772
- PMCID: PMC2908267
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.23427
The anti-inflammatory effects of adiponectin are mediated via a heme oxygenase-1-dependent pathway in rat Kupffer cells
Abstract
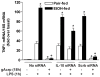
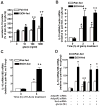
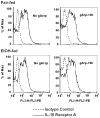
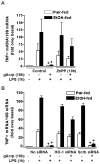
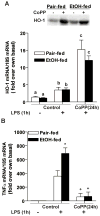
Altered expression and activity of immunomodulatory cytokines plays a major role in the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease. Chronic ethanol feeding increases the sensitivity of Kupffer cells, the resident hepatic macrophage, to lipopolysaccharide (LPS), leading to increased tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) expression. This sensitization is normalized by treatment of primary cultures of Kupffer cells with adiponectin, an anti-inflammatory adipokine. Here we tested the hypothesis that adiponectin-mediated suppression of LPS signaling in Kupffer cells is mediated via an interleukin-10 (IL-10)/heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) pathway after chronic ethanol feeding. Knockdown of IL-10 expression in primary cultures of Kupffer cells with small interfering RNA (siRNA) prevented the inhibitory effect of globular adiponectin (gAcrp) on LPS-stimulated TNF-alpha expression. gAcrp increased IL-10 mRNA and protein expression, as well as expression of the IL-10 inducible gene, HO-1; expression was higher in Kupffer cells from ethanol-fed rats compared with pair-fed controls. Although IL-10 receptor surface expression on Kupffer cells was not affected by ethanol feeding, IL-10-mediated phosphorylation of STAT3 and expression of HO-1 was higher in Kupffer cells after ethanol feeding. Inhibition of HO-1 activity, either by treatment with the HO-1 inhibitor zinc protoporphyrin or by siRNA knockdown of HO-1, prevented the inhibitory effect of gAcrp on LPS-stimulated TNF-alpha expression in Kupffer cells. LPS-stimulated TNF-alpha expression in liver was increased in mice after chronic ethanol exposure. When mice were treated with cobalt protoporphyrin to induce HO-1 expression, ethanol-induced sensitivity to LPS was ameliorated.
Conclusion: gAcrp prevents LPS-stimulated TNF-alpha expression in Kupffer cells through the activation of the IL-10/STAT3/HO-1 pathway. Kupffer cells from ethanol-fed rats are highly sensitive to the anti-inflammatory effects of gAcrp; this sensitivity is associated with both increased expression and sensitivity to IL-10.
Figures
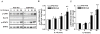
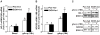
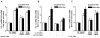
Similar articles
-
Adiponectin and heme oxygenase-1 suppress TLR4/MyD88-independent signaling in rat Kupffer cells and in mice after chronic ethanol exposure.J Immunol. 2010 Oct 15;185(8):4928-37. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002060. Epub 2010 Sep 22. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20861358 Free PMC article.
-
Adiponectin normalizes LPS-stimulated TNF-alpha production by rat Kupffer cells after chronic ethanol feeding.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006 May;290(5):G998-1007. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00553.2005. Epub 2006 Jan 12. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16410364 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism for adiponectin-dependent M2 macrophage polarization: link between the metabolic and innate immune activity of full-length adiponectin.J Biol Chem. 2011 Apr 15;286(15):13460-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.204644. Epub 2011 Feb 25. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21357416 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms for the anti-inflammatory effects of adiponectin in macrophages.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008 Mar;23 Suppl 1:S50-3. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2007.05284.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008. PMID: 18336664 Review.
-
Regulation of Kupffer cell activity during chronic ethanol exposure: role of adiponectin.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006 Oct;21 Suppl 3:S30-3. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04580.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006. PMID: 16958668 Review.
Cited by
-
What is the role of adiponectin in obesity related non-alcoholic fatty liver disease?World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Feb 14;19(6):802-12. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i6.802. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23430039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adiponectin inhibits inflammatory cytokines production by Beclin-1 phosphorylation and B-cell lymphoma 2 mRNA destabilization: role for autophagy induction.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Apr;175(7):1066-1084. doi: 10.1111/bph.14144. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29333604 Free PMC article.
-
Microglial Polarization and Inflammatory Mediators After Intracerebral Hemorrhage.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Apr;54(3):1874-1886. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9785-6. Epub 2016 Feb 19. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 26894396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of inflammatory responses and development of insulin resistance: how are they interlinked?J Biomed Sci. 2016 Dec 3;23(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12929-016-0303-y. J Biomed Sci. 2016. PMID: 27912756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of heme oxygenase expression by alcohol, hypoxia and oxidative stress.World J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 26;2(12):252-60. doi: 10.4331/wjbc.v2.i12.252. World J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 22216371 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vidali M, Stewart SF, Albano E. Interplay between oxidative stress and immunity in the progression of alcohol-mediated liver injury. Trends Mol Med. 2008;14:63–71. - PubMed
-
- Le Moine O, Marchant A, De Groote D, Azar C, Goldman M, Deviere J. Role of defective monocyte interleukin-10 release in tumor necrosis factor-alpha overproduction in alcoholics cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1995;22:1436–1439. - PubMed
-
- Hill DB, D’Souza NB, Lee EY, Burikhanov R, Deaciuc IV, de Villiers WJ. A role for interleukin-10 in alcohol-induced liver sensitization to bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2002;26:74–82. - PubMed
-
- Berg AH, Combs TP, Scherer PE. ACRP30/adiponectin: an adipokine regulating glucose and lipid metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2002;13:84–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
