The phenotype of murine wound macrophages
- PMID: 20052800
- PMCID: PMC2801619
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.0409236
The phenotype of murine wound macrophages
Abstract
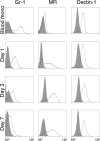
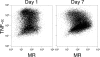
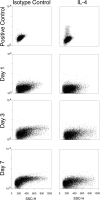
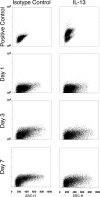
The phenotype of wound macrophages has not been studied by direct examination of these cells, yet macrophages recruited to sites of injury are described as alternatively activated macrophages, requiring IL-4 or IL-13 for phenotypic expression. This study characterized wound macrophage phenotype in the PVA sponge wound model in mice. Eighty-five percent of wound macrophages isolated 1 day after injury expressed Gr-1, but only 20% of those isolated at 7 days expressed this antigen. Macrophages from 1-, 3-, and 7-day wounds expressed markers of alternative activation,including mannose receptor, dectin-1, arginase 1,and Ym1, but did not contain iNOS. Day 1 wound macrophages produced more TNF-alpha, more IL-6, and less TGF-beta than Day 7 wound macrophages. Wound macrophages did not produce IL-10. The cytokines considered necessary for alternative activation of macrophages,IL-4 and IL-13, were not detected in the wound environment and were not produced by wound cells.Wound macrophages did not contain PStat6. Wound fluids inhibited IL-13-dependent phosphorylation of Stat6 and contained IL-13Ralpha2, a soluble decoy receptor for IL-13. The phenotype of wound macrophages was not altered in mice lacking IL-4Ralpha, which is required for Stat6-dependent signaling of IL-4 and IL-13.Wound macrophages exhibit a complex phenotype,which includes traits associated with alternative and classical activation and changes as the wound matures.The wound macrophage phenotype does not require IL-4 or IL-13.
Figures





Comment in
-
Editorial: macrophage functional phenotypes: no alternatives in dermal wound healing?J Leukoc Biol. 2010 Jan;87(1):19-21. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0509311. J Leukoc Biol. 2010. PMID: 20047887 No abstract available.
References
-
- Kodelja V, Muller C, Tenorio S, Schebesch C, Orfanos C E, Goerdt S. Differences in angiogenic potential of classically vs alternatively activated macrophages. Immunobiology. 1997;197:478–493. - PubMed
-
- Gordon S. Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:23–35. - PubMed
-
- Gordon S, Taylor P R. Monocyte and macrophage heterogeneity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:953–964. - PubMed
-
- Martinez F O, Helming L, Gordon S. Alternative activation of macrophages: an immunologic functional perspective. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:451–483. - PubMed
-
- Raes G, De Baetselier P, Noel W, Beschin A, Brombacher F, Hassanzadeh Gh G. Differential expression of FIZZ1 and Ym1 in alternatively versus classically activated macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 2002;71:597–602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

