Systems in development: motor skill acquisition facilitates three-dimensional object completion
- PMID: 20053012
- PMCID: PMC2805173
- DOI: 10.1037/a0014618
Systems in development: motor skill acquisition facilitates three-dimensional object completion
Abstract
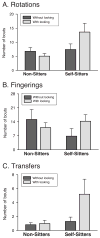
How do infants learn to perceive the backs of objects that they see only from a limited viewpoint? Infants' 3-dimensional object completion abilities emerge in conjunction with developing motor skills--independent sitting and visual-manual exploration. Infants at 4.5 to 7.5 months of age (n = 28) were habituated to a limited-view object and tested with volumetrically complete and incomplete (hollow) versions of the same object. Parents reported infants' sitting experience, and infants' visual-manual exploration of objects was observed in a structured play session. Infants' self-sitting experience and visual-manual exploratory skills predicted looking at the novel, incomplete object on the habituation task. Further analyses revealed that self-sitting facilitated infants' visual inspection of objects while they manipulated them. The results are framed within a developmental systems approach, wherein infants' sitting skill, multimodal object exploration, and object knowledge are linked in developmental time.
Copyright 2009 APA, all rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Adolph KE. Learning to keep balance. In: Kail R, editor. Advances in child development and behavior. Vol. 30. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science; 2002. pp. 1–40. - PubMed
-
- Adolph KE, Badaly D, Garciaguirre JS, Sotsky R. 15,000 steps: Infants’ locomotor experience. 2008. Manuscript in preparation.
-
- Adolph KE, Eppler MA, Marin L, Weise IB, Clearfield MW. Exploration in the service of prospective control. Infant Behavior & Development. 2000;23:441–460.
-
- Arterberry ME, Yonas A. Infants’ sensitivity to kinetic information for three-dimensional object shape. Perception & Psychophysics. 1988;44:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Arterberry ME, Yonas A. Perception of three-dimensional shape specified by optic flow by 8-week-old infants. Perception & Psychophysics. 2000;62:550–556. - PubMed

