A pre-operative elevated neutrophil: lymphocyte ratio does not predict survival from oesophageal cancer resection
- PMID: 20053279
- PMCID: PMC2819243
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-7819-8-1
A pre-operative elevated neutrophil: lymphocyte ratio does not predict survival from oesophageal cancer resection
Abstract
Background: Elevated pre-operative neutrophil: lymphocyte ratio (NLR) has been identified as a predictor of survival in patients with hepatocellular and colorectal cancer. The aim of this study was to examine the prognostic value of an elevated preoperative NLR following resection for oesophageal cancer.
Methods: Patients who underwent resection for oesophageal carcinoma from June 1997 to September 2007 were identified from a local cancer database. Data on demographics, conventional prognostic markers, laboratory analyses including blood count results, and histopathology were collected and analysed.
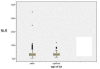
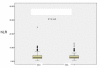
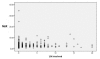
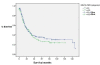
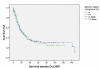
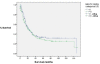
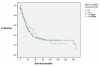
Results: A total of 294 patients were identified with a median age at diagnosis of 65.2 (IQR 59-72) years. The median pre-operative time of blood sample collection was three days (IQR 1-8). The median neutrophil count was 64.2 x 10-9/litre, median lymphocyte count 23.9 x 10-9/litre, whilst the NLR was 2.69 (IQR 1.95-4.02). NLR did not prove to be a significant predictor of number of involved lymph nodes (Cox regression, p = 0.754), disease recurrence (p = 0.288) or death (Cox regression, p = 0.374). Furthermore, survival time was not significantly different between patients with high (>or= 3.5) or low (< 3.5) NLR (p = 0.49).
Conclusion: Preoperative NLR does not appear to offer useful predictive ability for outcome, disease-free and overall survival following oesophageal cancer resection.
Figures
References
-
- Omloo JM, Sloof GW, Boellaard R, Hoekstra OS, Jager PL, van Dullemen HM, Fockens P, Plukker JT, van Lanschot JJ. Importance of fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) and endoscopic ultrasonography parameters in predicting survival following surgery for esophageal cancer. Endoscopy. 2008;40(6):464–471. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1077302. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

