A comparison of HLA-identical sibling allogeneic versus autologous transplantation for diffuse large B cell lymphoma: a report from the CIBMTR
- PMID: 20053330
- PMCID: PMC2929576
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2009.08.011
A comparison of HLA-identical sibling allogeneic versus autologous transplantation for diffuse large B cell lymphoma: a report from the CIBMTR
Abstract
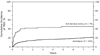
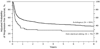
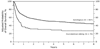
We compared outcomes of 916 diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients aged >or=18 years undergoing first autologous (n = 837) or myeloablative (MA) allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant (HCT) (n = 79) between 1995 and 2003 reported to the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR). Median follow-up was 81 months for allogeneic HCT versus 60 months for autologous HCT. Allogeneic HCT recipients were more likely to have high-risk disease features including higher stage, more prior chemotherapy regimens, and resistant disease. Allogeneic HCT was associated with a higher 1 year treatment-related mortality (TRM) (relative risk [RR] 4.88, 95% confidence interval [CI], 3.21-7.40, P < .001), treatment failure (RR 2.06, 95% CI, 1.54-2.75, P < .001), and mortality (RR 2.75, 95% CI, 2.03-3.72, P < .001). Risk of disease progression was similar in the 2 groups (RR 1.12, 95% CI, 0.73-1.72, P = .59). In fact, for 1-year survivors, no significant differences were observed for TRM, progression, progression-free (PFS) or overall survival (OS). Increased risks of TRM and mortality were associated with older age (>50 years), lower performance score, chemoresistance, and earlier year of transplant. In a cohort of mainly high-risk DLBCL patients, upfront MA allogeneic HCT, although associated with increased early mortality, was associated with a similar risk of disease progression compared to lower risk patients receiving autologous HCT.
Copyright (c) 2010 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Coiffier B, Lepage E, Briere J, et al. CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:235–242. - PubMed
-
- Feugier P, Van Hoof A, Sebban C, et al. Long-term results of the R-CHOP study in the treatment of elderly patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a study by the Groupe d'Etude des Lymphomes de l'Adulte. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:4117–4126. - PubMed
-
- Pfreundschuh M, Trumper L, Osterborg A, et al. CHOP-like chemotherapy plus rituximab versus CHOP-like chemotherapy alone in young patients with good-prognosis diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma: a randomised controlled trial by the MabThera International Trial (MInT) Group. Lancet Oncol. 2006;7:379–391. - PubMed
-
- Blay J, Gomez F, Sebban C, et al. The International Prognostic Index correlates to survival in patients with aggressive lymphoma in relapse: analysis of the PARMA trial. Parma Group. Blood. 1998;92:3562–3568. - PubMed
-
- Nademanee A, Molina A, Dagis A, et al. Autologous stem-cell transplantation for poor-risk and relapsed intermediate- and high-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Clin Lymphoma. 2000;1:46–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

