17β-Estradiol regulates insulin-degrading enzyme expression via an ERβ/PI3-K pathway in hippocampus: relevance to Alzheimer's prevention
- PMID: 20053478
- PMCID: PMC2889185
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2009.12.010
17β-Estradiol regulates insulin-degrading enzyme expression via an ERβ/PI3-K pathway in hippocampus: relevance to Alzheimer's prevention
Abstract
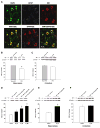
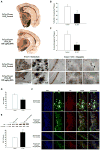
Insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE), an enzyme that primarily degrades insulin, has recently been demonstrated to play a significant role in the catabolism of amyloid β (Aβ) protein in the brain. Reduced IDE expression and/or activity have been associated with the etiology and development of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Using three model systems, the present investigation provides the first documentation indicating that estrogen robustly regulates the expression of IDE in normal, menopausal and early-stage AD brains. In vitro analyses in primary cultures of rat hippocampal neurons revealed that 17β-estradiol (17β-E2) increased IDE in both mRNA and protein levels in a time-dependent manner. Further pharmacological analyses indicated that 17β-E2-induced IDE expression was dependent upon estrogen receptor (ER) β and required activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-K). In vivo analyses in adult female rats revealed a brain region-specific responsive profile. Ovariectomy (OVX) induced a significant decline in IDE expression in the hippocampus, which was prevented by 17β-E2. Neither OVX nor 17β-E2 affected IDE expression in the cerebellum. In vivo analyses in triple transgenic AD (3xTg-AD) female mice revealed an inverse correlation between the age-related increase in Aβ load and the decrease in IDE expression in the hippocampal formation. Treatment with 17β-E2 attenuated Aβ accumulation/plaque formation and elevated hippocampal IDE expression in 12-month-old 3xTg-AD OVX mice. Collectively, these findings indicate that 17β-E2 regulates IDE expression in a brain region-specific manner and such a regulatory role in the hippocampus, mediated by an ERβ/PI3-K pathway, could serve as a direct mechanism underlying estrogen-mediated preventative effect against AD when initiated at the onset of menopause.
Copyright © 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose. The use of animals was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the University of Southern California.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Insulin-degrading enzyme as a downstream target of insulin receptor signaling cascade: implications for Alzheimer's disease intervention.J Neurosci. 2004 Dec 8;24(49):11120-6. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2860-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15590928 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates the levels of insulin, amyloid beta-protein, and the beta-amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Apr 1;100(7):4162-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0230450100. Epub 2003 Mar 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12634421 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction in Aβ-induced cell death in the hippocampus of 17β-estradiol-treated female rats is associated with an increase in IGF-I signaling and somatostatinergic tone.J Neurochem. 2015 Dec;135(6):1257-71. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13381. Epub 2015 Nov 6. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 26442993
-
Insulin, insulin-degrading enzyme and amyloid-beta peptide in Alzheimer's disease: review and hypothesis.Neurobiol Aging. 2006 Feb;27(2):190-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.01.004. Epub 2005 Feb 17. Neurobiol Aging. 2006. PMID: 16399206 Review.
-
Role of estrogen replacement therapy in memory enhancement and the prevention of neuronal loss associated with Alzheimer's disease.Am J Med. 1997 Sep 22;103(3A):19S-25S. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(97)00260-x. Am J Med. 1997. PMID: 9344403 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting estrogen receptors for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2014 Feb;49(1):39-49. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8484-9. Epub 2013 Jun 16. Mol Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 23771838 Review.
-
Sex differences in the progression to Alzheimer's disease: a combination of functional and structural markers.Geroscience. 2024 Apr;46(2):2619-2640. doi: 10.1007/s11357-023-01020-z. Epub 2023 Dec 18. Geroscience. 2024. PMID: 38105400 Free PMC article.
-
Age-dependent regulation of obesity and Alzheimer-related outcomes by hormone therapy in female 3xTg-AD mice.PLoS One. 2017 Jun 2;12(6):e0178490. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178490. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28575011 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term pioglitazone treatment improves learning and attenuates pathological markers in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;30(4):943-61. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2012-111661. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012. PMID: 22495349 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen and insulin transport through the blood-brain barrier.Physiol Behav. 2016 Sep 1;163:312-321. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2016.05.019. Epub 2016 May 13. Physiol Behav. 2016. PMID: 27182046 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Authier F, Posner BI, Bergeron JJ. Insulin-degrading enzyme. Clin Invest Med. 1996;19:149–160. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein HG, Ansorge S, Riederer P, Reiser M, Frolich L, Bogerts B. Insulin-degrading enzyme in the Alzheimer’s disease brain: prominent localization in neurons and senile plaques. Neurosci Lett. 1999;263:161–164. - PubMed
-
- Bertram L, Blacker D, Mullin K, Keeney D, Jones J, Basu S, Yhu S, McInnis MG, Go RC, Vekrellis K, Selkoe DJ, Saunders AJ, Tanzi RE. Evidence for genetic linkage of Alzheimer’s disease to chromosome 10q. Science. 2000;290:2302–2303. - PubMed
-
- Bian L, Yang JD, Guo TW, Sun Y, Duan SW, Chen WY, Pan YX, Feng GY, He L. Insulin-degrading enzyme and Alzheimer disease: a genetic association study in the Han Chinese. Neurology. 2004;63:241–245. - PubMed
-
- Bjork BF, Katzov H, Kehoe P, Fratiglioni L, Winblad B, Prince JA, Graff C. Positive association between risk for late-onset Alzheimer disease and genetic variation in IDE. Neurobiol Aging. 2007;28:1374–1380. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

