Mechanisms of mosaicism, chimerism and uniparental disomy identified by single nucleotide polymorphism array analysis
- PMID: 20053666
- PMCID: PMC3146011
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddq003
Mechanisms of mosaicism, chimerism and uniparental disomy identified by single nucleotide polymorphism array analysis
Abstract
Mosaic aneuploidy and uniparental disomy (UPD) arise from mitotic or meiotic events. There are differences between these mechanisms in terms of (i) impact on embryonic development; (ii) co-occurrence of mosaic trisomy and UPD and (iii) potential recurrence risks. We used a genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) array to study patients with chromosome aneuploidy mosaicism, UPD and one individual with XX/XY chimerism to gain insight into the developmental mechanism and timing of these events. Sixteen cases of mosaic aneuploidy originated mitotically, and these included four rare trisomies and all of the monosomies, consistent with the influence of selective factors. Five trisomies arose meiotically, and three of the five had UPD in the disomic cells, confirming increased risk for UPD in the case of meiotic non-disjunction. Evidence for the meiotic origin of aneuploidy and UPD was seen in the patterns of recombination visible during analysis with 1-3 crossovers per chromosome. The mechanisms of formation of the UPD included trisomy rescue, with and without concomitant trisomy, monosomy rescue, and mitotic formation of a mosaic segmental UPD. UPD was also identified in an XX/XY chimeric individual, with one cell line having complete maternal UPD consistent with a parthenogenetic origin. Utilization of SNP arrays allows simultaneous evaluation of genomic alterations and insights into aneuploidy and UPD mechanisms. Differentiation of mitotic and meiotic origins for aneuploidy and UPD supports existence of selective factors against full trisomy of some chromosomes in the early embryo and provides data for estimation of recurrence and disease mechanisms.
Figures


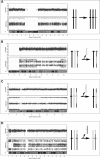
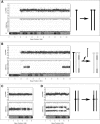

References
-
- Hassold T.J., Jacobs P.A. Trisomy in man. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1984;18:69–97. - PubMed
-
- Hassold T., Hall H., Hunt P. The origin of human aneuploidy: where we have been, where we are going. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007;16(Spec No. 2):R203–R208. - PubMed
-
- Kalousek D.K. Pathogenesis of chromosomal mosaicism and its effect on early human development. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2000;91:39–45. - PubMed
-
- Engel E. A fascination with chromosome rescue in uniparental disomy: Mendelian recessive outlaws and imprinting copyrights infringements. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2006;14:1158–1169. - PubMed
-
- Kotzot D. Complex and segmental uniparental disomy updated. J. Med. Genet. 2008;45:545–556. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

