Intracellular targeting signals and lipid specificity determinants of the ALA/ALIS P4-ATPase complex reside in the catalytic ALA alpha-subunit
- PMID: 20053675
- PMCID: PMC2828965
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-08-0656
Intracellular targeting signals and lipid specificity determinants of the ALA/ALIS P4-ATPase complex reside in the catalytic ALA alpha-subunit
Abstract
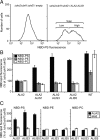
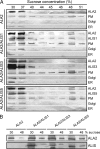
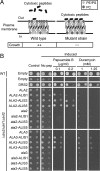
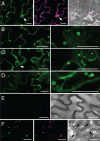
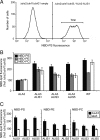
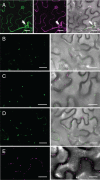
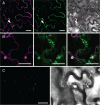
Members of the P(4) subfamily of P-type ATPases are believed to catalyze flipping of phospholipids across cellular membranes, in this way contributing to vesicle biogenesis in the secretory and endocytic pathways. P(4)-ATPases form heteromeric complexes with Cdc50-like proteins, and it has been suggested that these act as beta-subunits in the P(4)-ATPase transport machinery. In this work, we investigated the role of Cdc50-like beta-subunits of P(4)-ATPases for targeting and function of P(4)-ATPase catalytic alpha-subunits. We show that the Arabidopsis P(4)-ATPases ALA2 and ALA3 gain functionality when coexpressed with any of three different ALIS Cdc50-like beta-subunits. However, the final cellular destination of P(4)-ATPases as well as their lipid substrate specificity are independent of the nature of the ALIS beta-subunit they were allowed to interact with.
Figures

References
-
- Axelsen K. B., Palmgren M. G. Evolution of substrate specificities in the P-type ATPase superfamily. J. Mol. Evol. 1998;46:84–101. - PubMed
-
- Brandizzi F., Fricker M., Hawes C. A greener world: the revolution in plant bioimaging. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002;3:520–530. - PubMed
-
- Chantalat S., Park S. K., Hua Z., Liu K., Gobin R., Peyroche A., Rambourg A., Graham T. R., Jackson C. L. The Arf activator Gea2p and the P-type ATPase Drs2p interact at the Golgi in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Cell Sci. 2004;117:711–722. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

