Structural mutants of the spindle pole body cause distinct alteration of cytoplasmic microtubules and nuclear dynamics in multinucleated hyphae
- PMID: 20053682
- PMCID: PMC2828962
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e09-07-0555
Structural mutants of the spindle pole body cause distinct alteration of cytoplasmic microtubules and nuclear dynamics in multinucleated hyphae
Abstract
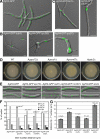
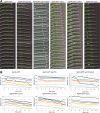
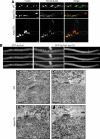
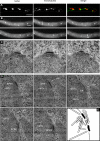
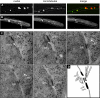
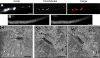
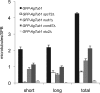
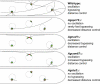
In the multinucleate fungus Ashbya gossypii, cytoplasmic microtubules (cMTs) emerge from the spindle pole body outer plaque (OP) in perpendicular and tangential directions. To elucidate the role of cMTs in forward/backward movements (oscillations) and bypassing of nuclei, we constructed mutants potentially affecting cMT nucleation or stability. Hyphae lacking the OP components AgSpc72, AgNud1, AgCnm67, or the microtubule-stabilizing factor AgStu2 grew like wild- type but showed substantial alterations in the number, length, and/or nucleation sites of cMTs. These mutants differently influenced nuclear oscillation and bypassing. In Agspc72Delta, only long cMTs were observed, which emanate tangentially from reduced OPs; nuclei mainly moved with the cytoplasmic stream but some performed rapid bypassing. Agnud1Delta and Agcnm67Delta lack OPs; short and long cMTs emerged from the spindle pole body bridge/half-bridge structures, explaining nuclear oscillation and bypassing in these mutants. In Agstu2Delta only very short cMTs emanated from structurally intact OPs; all nuclei moved with the cytoplasmic stream. Therefore, long tangential cMTs promote nuclear bypassing and short cMTs are important for nuclear oscillation. Our electron microscopy ultrastructural analysis also indicated that assembly of the OP occurs in a stepwise manner, starting with AgCnm67, followed by AgNud1 and lastly AgSpc72.
Figures

References
-
- Ayad-Durieux Y., Knechtle P., Goff S., Dietrich F., Philippsen P. A PAK-like protein kinase is required for maturation of young hyphae and septation in the filamentous ascomycete Ashbya gossypii. J. Cell Sci. 2000;113:4563–4575. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

