Quadruplex structures of muscle gene promoter sequences enhance in vivo MyoD-dependent gene expression
- PMID: 20053730
- PMCID: PMC2853122
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp1208
Quadruplex structures of muscle gene promoter sequences enhance in vivo MyoD-dependent gene expression
Abstract
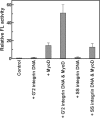
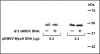
Gene promoters are enriched in guanine clusters that potentially fold into quadruplex structures. Such quadruplexes were implicated in the regulation of gene expression, plausibly by interacting with transcription factors. We showed previously that homodimers of the myogenic transcription factor MyoD bound in vitro most tightly bimolecular quadruplexes of promoter sequences of muscle-specific genes. By contrast, MyoD-E47 heterodimers formed tighter complexes with d(CANNTG) E-box motifs that govern muscle gene expression. Here, we show that DNA quadruplexes enhance in vivo MyoD and E-box-driven expression of a firefly luciferase (FL) reporter gene. HEK293 cells were transfected with FL expressing p4RTK-FL vector alone or together with MyoD expressing pEMSV-MyoD plasmid, with quadruplexes of alpha7 integrin or sarcomeric mitochondrial creatine kinase (sMtCK) muscle gene promoters or with a combination thereof. Whereas MyoD elevated by approximately 10-fold the levels of FL mRNA and protein, the DNA quadruplexes by themselves did not affect FL expression. However, together with MyoD, quadruplex DNA increased by approximately 35-fold the amounts of FL mRNA and protein. Without affecting its expression, DNA quadruplexes bound MyoD in the cells. Based on these results, we propose models for the regulation of muscle gene transcription by direct interaction of MyoD with promoter quadruplex structures.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MyoD uses overlapping but distinct elements to bind E-box and tetraplex structures of regulatory sequences of muscle-specific genes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(21):7087-95. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm746. Epub 2007 Oct 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17942416 Free PMC article.
-
Formation and properties of hairpin and tetraplex structures of guanine-rich regulatory sequences of muscle-specific genes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 May 20;33(9):2887-900. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki606. Print 2005. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15908587 Free PMC article.
-
Homodimeric MyoD preferentially binds tetraplex structures of regulatory sequences of muscle-specific genes.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jul 22;280(29):26805-12. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M500820200. Epub 2005 May 27. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15923190
-
Differential binding of quadruplex structures of muscle-specific genes regulatory sequences by MyoD, MRF4 and myogenin.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jul;36(12):3916-25. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn340. Epub 2008 May 29. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18511462 Free PMC article.
-
The circuitry of a master switch: Myod and the regulation of skeletal muscle gene transcription.Development. 2005 Jun;132(12):2685-95. doi: 10.1242/dev.01874. Development. 2005. PMID: 15930108 Review.
Cited by
-
The evolving world of protein-G-quadruplex recognition: a medicinal chemist's perspective.Biochimie. 2011 Aug;93(8):1219-30. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2011.04.018. Epub 2011 Apr 29. Biochimie. 2011. PMID: 21549174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long promoter sequences form higher-order G-quadruplexes: an integrative structural biology study of c-Myc, k-Ras and c-Kit promoter sequences.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Apr 22;50(7):4127-4147. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac182. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35325198 Free PMC article.
-
TMPyP4, a Stabilizer of Nucleic Acid Secondary Structure, Is a Novel Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 24;10(9):e0139167. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139167. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26402367 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Binding Specificity among bHLH Transcription Factors.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 24;22(17):9150. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179150. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BmILF and i-motif structure are involved in transcriptional regulation of BmPOUM2 in Bombyx mori.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Feb 28;46(4):1710-1723. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1207. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29194483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buckingham M. Skeletal muscle formation in vertebrates. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2001;11:440–448. - PubMed
-
- Tajbakhsh S. Stem cells to tissue: molecular, cellular and anatomical heterogeneity in skeletal muscle. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2003;13:413–422. - PubMed
-
- Rudnicki MA, Jaenisch R. The MyoD family of transcription factors and skeletal myogenesis. Bioessays. 1995;17:203–209. - PubMed
-
- Pownall ME, Gustafsson MK, Emerson C.P., Jr Myogenic regulatory factors and the specification of muscle progenitors in vertebrate embryos. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2002;18:747–783. - PubMed

