Commandeering a biological pathway using aptamer-derived molecular adaptors
- PMID: 20053731
- PMCID: PMC2853121
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp1207
Commandeering a biological pathway using aptamer-derived molecular adaptors
Abstract
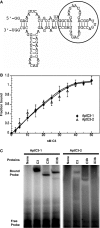
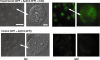
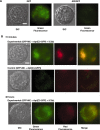
Induction of molecular proximity can mediate a discrete functional response in biological systems. Therefore, creating new and specific connectivity between non-interacting proteins is a means of imposing rational control over biological processes. According to this principle, here we use composite RNA aptamers to generate molecular adaptors that link various 'target' molecules to a common 'utility' molecule, with the utility molecule being an entry point to a pathway conscripted to process the target molecule. In particular, we created a bi-functional aptamer that simultaneously binds to the green fluorescent protein (serving as a surrogate extracellular target) and the opsonin C3b/iC3b (serving as the utility molecule). This bi-functional aptamer enabled us to commandeer the C3-based opsonization-phagocytosis pathway to selectively transport an extracellular target into the lysosome for degradation. This novel strategy has the potential for powerful therapeutic applications with extracellular proteins involved in tumor development or surface markers on cancer cells as the target molecules.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Opsonization of yeast cells with equine iC3b, C3b, and IgG.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2001 Aug 10;80(3-4):209-23. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2427(01)00262-8. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2001. PMID: 11457475
-
Phosphorylation of C3 by a casein kinase released from activated human platelets increases opsonization of immune complexes and binding to complement receptor type 1.Eur J Immunol. 2001 Apr;31(4):1047-54. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200104)31:4<1047::aid-immu1047>3.0.co;2-y. Eur J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11298329
-
Complement-Mediated Selective Tumor Cell Lysis Enabled by Bi-Functional RNA Aptamers.Genes (Basel). 2021 Dec 29;13(1):86. doi: 10.3390/genes13010086. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35052426 Free PMC article.
-
A molecular basis of activation of the alternative pathway of human complement.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1979;120B:3-17. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1979. PMID: 390986 Review.
-
Macrophage complement receptors and pathogen clearance.Cell Microbiol. 2007 Sep;9(9):2095-102. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.00981.x. Epub 2007 Jun 21. Cell Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17590164 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and classification of RNA aptamers for therapeutic purposes: an updated review with emphasis on cancer.Mol Cell Biochem. 2023 Jul;478(7):1573-1598. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04614-x. Epub 2022 Nov 24. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36434145 Review.
-
RNA aptamers targeted for human αA-crystallin do not bind αB-crystallin, and spare the α-crystallin domain.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Sep 16;491(2):423-428. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.07.085. Epub 2017 Jul 15. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 28720498 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting the Uncertain Future of Aptamer-Based Diagnostics and Therapeutics.Molecules. 2015 Apr 16;20(4):6866-87. doi: 10.3390/molecules20046866. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 25913927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In search of novel drug target sites on estrogen receptors using RNA aptamers.Nucleic Acid Ther. 2014 Jun;24(3):226-38. doi: 10.1089/nat.2013.0474. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2014. PMID: 24588102 Free PMC article.
-
Aptamer-targeted antigen delivery.Mol Ther. 2014 Jul;22(7):1375-1387. doi: 10.1038/mt.2014.51. Epub 2014 Mar 31. Mol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24682172 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aderem A, Underhill DM. Mechanisms of phagocytosis in macrophages. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1999;17:593–623. - PubMed
-
- Janssen BJ, Christodoulidou A, McCarthy A, Lambris JD, Gros P. Structure of C3b reveals conformational changes that underlie complement activity. Nature. 2006;444:213–216. - PubMed
-
- Wiesmann C, Katschke KJ, Yin J, Helmy KY, Steffek M, Fairbrother WJ, McCallum SA, Embuscado L, DeForge L, Hass PE, et al. Structure of C3b in complex with CRIg gives insights into regulation of complement activation. Nature. 2006;444:217–220. - PubMed
-
- Abdul Ajees A, Gunasekaran K, Volanakis JE, Narayana SV, Kotwal GJ, Murthy HM. The structure of complement C3b provides insights into complement activation and regulation. Nature. 2006;444:221–225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

