The hepatitis B virus X protein modulates hepatocyte proliferation pathways to stimulate viral replication
- PMID: 20053744
- PMCID: PMC2826060
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02196-09
The hepatitis B virus X protein modulates hepatocyte proliferation pathways to stimulate viral replication
Abstract
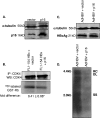
Worldwide, there are over 350 million people who are chronically infected with the human hepatitis B virus (HBV); chronic HBV infections are associated with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The results of various studies suggest that the HBV X protein (HBx) has a role in the development of HBV-associated HCC. HBx can regulate numerous cellular signal transduction pathways, including those that modulate cell proliferation. Many previous studies that analyzed the impact of HBx on cell proliferation pathways were conducted using established or immortalized cell lines, and when HBx was expressed in the absence of HBV replication, and the precise effect of HBx on these pathways has often differed depending on experimental conditions. We have studied the effect of HBx on cell proliferation in cultured primary rat hepatocytes, a biologically relevant system. We demonstrate that HBx, both by itself and in the context of HBV replication, affected the levels and activities of various cell cycle-regulatory proteins to induce normally quiescent hepatocytes to enter the G(1) phase of the cell cycle but not to proceed to S phase. We linked HBx regulation of cell proliferation to cytosolic calcium signaling and HBx stimulation of HBV replication. Cumulatively, our studies suggest that HBx induces normally quiescent hepatocytes to enter the G(1) phase of the cell cycle and that this calcium-dependent HBx activity is required for HBV replication. These studies identify an essential function of HBx during HBV replication and a mechanism that may connect HBV infections to the development of HCC.
Figures

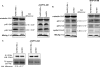
Similar articles
-
Hepatitis B virus modulates store-operated calcium entry to enhance viral replication in primary hepatocytes.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 2;12(2):e0168328. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168328. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28151934 Free PMC article.
-
The hepatitis B virus HBx protein modulates cell cycle regulatory proteins in cultured primary human hepatocytes.Virus Res. 2011 Jan;155(1):363-7. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.09.023. Epub 2010 Oct 8. Virus Res. 2011. PMID: 20934470 Free PMC article.
-
The C-terminal region of the hepatitis B virus X protein is required for its stimulation of HBV replication in primary mouse hepatocytes.Virus Res. 2012 May;165(2):170-8. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2012.02.013. Epub 2012 Feb 23. Virus Res. 2012. PMID: 22387566
-
Modulation of apoptotic signaling by the hepatitis B virus X protein.Viruses. 2012 Nov 8;4(11):2945-72. doi: 10.3390/v4112945. Viruses. 2012. PMID: 23202511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular functions and biological roles of hepatitis B virus x protein.Cancer Sci. 2006 Oct;97(10):977-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00299.x. Cancer Sci. 2006. PMID: 16984372 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An in vitro Study on the Role of Hepatitis B Virus X Protein C-Terminal Truncation in Liver Disease Development.Front Genet. 2021 Mar 12;12:633341. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.633341. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33777103 Free PMC article.
-
The hepatitis B virus X protein elevates cytosolic calcium signals by modulating mitochondrial calcium uptake.J Virol. 2012 Jan;86(1):313-27. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06442-11. Epub 2011 Oct 26. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22031934 Free PMC article.
-
Biotic activity of Ca(2+)-modulating non-traditional antimicrobial and -viral agents.Front Microbiol. 2013 Dec 12;4:381. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00381. eCollection 2013. Front Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24376441 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Transcriptome-Wide Analysis of Hepatitis B Virus-Mediated Changes to Normal Hepatocyte Gene Expression.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Feb 18;12(2):e1005438. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005438. eCollection 2016 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 26891448 Free PMC article.
-
Survivin expression starts before hepatocellular cancer development in the liver of chronic hepatitis B patients: a pilot, cross-sectional study.Prz Gastroenterol. 2020;15(2):138-143. doi: 10.5114/pg.2019.87081. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Prz Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32550946 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn, J. Y., E. Y. Chung, H. J. Kwun, and K. L. Jang. 2001. Transcriptional repression of p21(waf1) promoter by hepatitis B virus X protein via a p53-independent pathway. Gene 275:163-168. - PubMed
-
- Beasley, R. P., L.-Y. Hwang, C.-C. Lin, and C.-S. Chien. 1981. Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus. A prospective study of 22,707 men in Taiwan. Lancet ii(8256):1129-1133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

