Leukemia-initiating cells from some acute myeloid leukemia patients with mutated nucleophosmin reside in the CD34(-) fraction
- PMID: 20053758
- PMCID: PMC2837317
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2009-02-206565
Leukemia-initiating cells from some acute myeloid leukemia patients with mutated nucleophosmin reside in the CD34(-) fraction
Abstract
Leukemia-initiating cells (LICs) in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) are believed to be restricted to the CD34(+) fraction. However, one of the most frequently mutated genes in AML is nucleophosmin (NPM), and this is associated with low CD34 expression. We, therefore, investigated whether NPM-mutated AMLs have LICs restricted to the CD34(+) fraction. We transplanted sorted fractions of primary NPM-mutated AML into immunodeficient mice to establish which fractions initiate leukemia. Approximately one-half of cases had LICs exclusively within the CD34(-) fraction, whereas the CD34(+) fraction contained normal multilineage hematopoietic repopulating cells. Most of the remaining cases had LICs in both CD34(+) and CD34(-) fractions. When samples were sorted based on CD34 and CD38 expression, multiple fractions initiated leukemia in primary and secondary recipients. The data indicate that the phenotype of LICs is more heterogeneous than previously realized and can vary even within a single sample. This feature of LICs may make them particularly difficult to eradicate using therapies targeted against surface antigens.
Figures
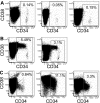

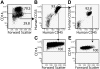
References
-
- Bonnet D, Dick JE. Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat Med. 1997;3(7):730–737. - PubMed
-
- Ishikawa F, Yoshida S, Saito Y, et al. Chemotherapy-resistant human AML stem cells home to and engraft within the bone-marrow endosteal region. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25(11):1315–1321. - PubMed
-
- Taussig DC, Miraki-Moud F, Anjos-Afonso F, et al. Anti-CD38 antibody-mediated clearance of human repopulating cells masks the heterogeneity of leukemia-initiating cells. Blood. 2008;112(3):568–575. - PubMed
-
- Falini B, Mecucci C, Tiacci E, et al. Cytoplasmic nucleophosmin in acute myelogenous leukemia with a normal karyotype. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(3):254–266. - PubMed
-
- Gale RE, Green C, Allen C, et al. The impact of FLT3 internal tandem duplication mutant level, number, size, and interaction with NPM1 mutations in a large cohort of young adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2008;111(5):2776–2784. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

