Multiplex-PCR method for species identification of coagulase-positive staphylococci
- PMID: 20053855
- PMCID: PMC2832457
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01232-09
Multiplex-PCR method for species identification of coagulase-positive staphylococci
Abstract
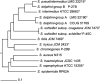
In veterinary medicine, coagulase-positive staphylococci (CoPS) other than Staphylococcus aureus have frequently been misidentified as being S. aureus strains, as they have several phenotypic traits in common. There has been no reliable method to distinguish among CoPS species in veterinary clinical laboratories. In the present study, we sequenced the thermonuclease (nuc) genes of staphylococcal species and devised a multiplex-PCR (M-PCR) method for species identification of CoPS by targeting the nuc gene locus. To evaluate sensitivity and specificity, we used this M-PCR method on 374 staphylococcal strains that had been previously identified to the species level by an hsp60 sequencing approach. We could successfully distinguish between S. aureus, S. hyicus, S. schleiferi, S. intermedius, S. pseudintermedius, and S. delphini groups A and B. The present method was both sensitive (99.8%) and specific (100%). Our M-PCR assay will allow the routine species identification of CoPS isolates from various animal species for clinical veterinary diagnosis.
Figures

References
-
- Aarestrup, F. M. 2001. Comparative ribotyping of Staphylococcus intermedius isolated from members of the Canoidea gives possible evidence for host-specificity and co-evolution of bacteria and hosts. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51:1343-1347. - PubMed
-
- Abraham, J. L., D. O. Morris, G. C. Griffeth, F. S. Shofer, and S. C. Rankin. 2007. Surveillance of healthy cats and cats with inflammatory skin disease for colonization of the skin by methicillin-resistant coagulase-positive staphylococci and Staphylococcus schleiferi ssp. schleiferi. Vet. Dermatol. 18:252-259. - PubMed
-
- Bannoehr, J., N. L. Ben Zakour, A. S. Waller, L. Guardabassi, K. L. Thoday, A. H. M. van den Broek, and J. R. Fitzgerald. 2007. Population genetic structure of the Staphylococcus intermedius group: insights into agr diversification and the emergence of methicillin-resistant strains. J. Bacteriol. 189:8685-8692. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bemis, D. A., R. D. Jones, L. E. Hiatt, E. D. Ofori, B. W. Rohrbach, L. A. Frank, and S. A. Kania. 2006. Comparison of tests to detect oxacillin resistance in Staphylococcus intermedius, Staphylococcus schleiferi, and Staphylococcus aureus isolates from canine hosts. J. Clin. Microbiol. 44:3374-3376. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

