Glutamatergic and nonglutamatergic neurons of the ventral tegmental area establish local synaptic contacts with dopaminergic and nondopaminergic neurons
- PMID: 20053904
- PMCID: PMC3209506
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3884-09.2010
Glutamatergic and nonglutamatergic neurons of the ventral tegmental area establish local synaptic contacts with dopaminergic and nondopaminergic neurons
Abstract
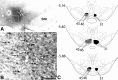
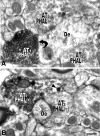
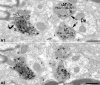
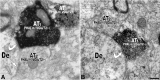
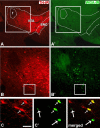
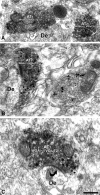
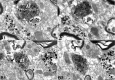
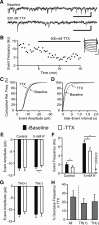
The ventral tegmental area (VTA) contributes to reward and motivation signaling. In addition to the well established populations of dopamine (DA) or GABA VTA neurons, glutamatergic neurons were recently discovered in the VTA. These glutamatergic neurons express the vesicular glutamate transporter 2, VGluT2. To investigate whether VTA glutamatergic neurons establish local synapses, we tagged axon terminals from resident VTA neurons by intra-VTA injection of Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin (PHA-L) or an adeno-associated virus encoding wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) and by immunoelectron microscopy determined the presence of VGluT2 in PHA-L- or WGA-positive terminals. We found that PHA-L- or WGA-positive terminals from tagged VTA cells made asymmetric or symmetric synapses within the VTA. VGluT2 immunoreactivity was detected in the vast majority of PHA-L- or WGA-positive terminals forming asymmetric synapses. These results indicate that both VTA glutamatergic and nonglutamatergic (likely GABAergic) neurons establish local synapses. To examine the possible DAergic nature of postsynaptic targets of VTA glutamatergic neurons, we did triple immunolabeling with antibodies against VGluT2, tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), and PHA-L. From triple-labeled tissue, we found that double-labeled PHA-L (+)/VGluT2 (+) axon terminals formed synaptic contacts on dendrites of both TH-positive and TH-negative cells. Consistent with these anatomical observations, in whole-cell slice recordings of VTA neurons we observed that blocking action potential activity significantly decreased the frequency of synaptic glutamatergic events in DAergic and non-DAergic neurons. These observations indicate that resident VTA glutamatergic neurons are likely to affect both DAergic and non-DAergic neurotransmission arising from the VTA.
Figures


References
-
- Bai L, Xu H, Collins JF, Ghishan FK. Molecular and functional analysis of a novel neuronal vesicular glutamate transporter. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:36764–36769. - PubMed
-
- Bayer VE, Pickel VM. GABA-labeled terminals form proportionally more synapses with dopaminergic neurons containing low densities of tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactivity in rat ventral tegmental area. Brain Res. 1991;559:44–55. - PubMed
-
- Berridge KC, Robinson TE. What is the role of dopamine in reward: hedonic impact, reward learning, or incentive salience? Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1998;28:309–369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
