Intracellular consequences of SOS1 deficiency during salt stress
- PMID: 20054031
- PMCID: PMC2826659
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erp391
Intracellular consequences of SOS1 deficiency during salt stress
Abstract
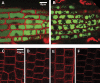
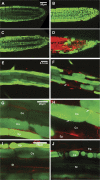
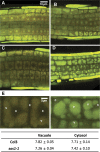
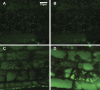
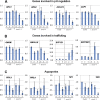
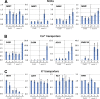
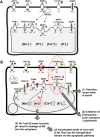
A mutation of AtSOS1 (Salt Overly Sensitive 1), a plasma membrane Na(+)/H(+)-antiporter in Arabidopsis thaliana, leads to a salt-sensitive phenotype accompanied by the death of root cells under salt stress. Intracellular events and changes in gene expression were compared during a non-lethal salt stress between the wild type and a representative SOS1 mutant, atsos1-1, by confocal microscopy using ion-specific fluorophores and by quantitative RT-PCR. In addition to the higher accumulation of sodium ions, atsos1-1 showed inhibition of endocytosis, abnormalities in vacuolar shape and function, and changes in intracellular pH compared to the wild type in root tip cells under stress. Quantitative RT-PCR revealed a dramatically faster and higher induction of root-specific Ca(2+) transporters, including several CAXs and CNGCs, and the drastic down-regulation of genes involved in pH-homeostasis and membrane potential maintenance. Differential regulation of genes for functions in intracellular protein trafficking in atsos1-1 was also observed. The results suggested roles of the SOS1 protein, in addition to its function as a Na(+)/H(+) antiporter, whose disruption affected membrane traffic and vacuolar functions possibly by controlling pH homeostasis in root cells.
Figures
Comment in
-
Consequences of SOS1 deficiency: intracellular physiology and transcription.Plant Signal Behav. 2010 Jun;5(6):766-8. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erp391.. Epub 2010 Jun 1. Plant Signal Behav. 2010. PMID: 20505347 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Apse MP, Aharon GS, Snedden WA, Blumwald E. Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+antiport in Arabidopsis. Science. 1999;285:1256–1258. - PubMed
-
- Apse MP, Sottosanto JB, Blumwald E. Vacuolar cation/H+exchange, ion homeostasis, and leaf development are altered in a T-DNA insertional mutant of AtNHX1, the Arabidopsis vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter. The Plant Journal. 2003;36:229–239. - PubMed
-
- Baumgartner M, Patel H, Barber DL. Na+/H+exchanger NHE1 as plasma membrane scaffold in the assembly of signaling complexes. American Journal of Physiology–Cell Physiology. 2004;287:C844–C850. - PubMed
-
- Cheng NH, Pittman JK, Zhu JK, Hirschi KD. The protein kinase SOS2 activates the Arabidopsis H+/Ca2+antiporter CAX1 to integrate calcium transport and salt tolerance. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2004;279:2922–2926. - PubMed
-
- Chinnusamy V, Zhu J, Zhu JK. Salt stress signaling and mechanisms of plant salt tolerance. Genetic Engineering. 2006;27:141–177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

