A high-resolution association mapping panel for the dissection of complex traits in mice
- PMID: 20054062
- PMCID: PMC2813484
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.099234.109
A high-resolution association mapping panel for the dissection of complex traits in mice
Abstract
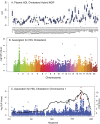
Systems genetics relies on common genetic variants to elucidate biologic networks contributing to complex disease-related phenotypes. Mice are ideal model organisms for such approaches, but linkage analysis has been only modestly successful due to low mapping resolution. Association analysis in mice has the potential of much better resolution, but it is confounded by population structure and inadequate power to map traits that explain less than 10% of the variance, typical of mouse quantitative trait loci (QTL). We report a novel strategy for association mapping that combines classic inbred strains for mapping resolution and recombinant inbred strains for mapping power. Using a mixed model algorithm to correct for population structure, we validate the approach by mapping over 2500 cis-expression QTL with a resolution an order of magnitude narrower than traditional QTL analysis. We also report the fine mapping of metabolic traits such as plasma lipids. This resource, termed the Hybrid Mouse Diversity Panel, makes possible the integration of multiple data sets and should prove useful for systems-based approaches to complex traits and studies of gene-by-environment interactions.
Figures
References
-
- Aherrahrou Z, Doehring LC, Ehlers EM, Liptau H, Depping R, Linsel-Nitschke P, Kaczmarek PM, Erdmann J, Schunkert H. An alternative splice variant in Abcc6, the gene causing dystrophic calcification, leads to protein deficiency in C3H/He mice. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:7608–7615. - PubMed
-
- Beck JA, Lloyd S, Hafezparast M, Lennon-Pierce M, Eppig JT, Festing MF, Fisher EM. Genealogies of mouse inbred strains. Nat Genet. 2000;24:23–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL28481/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG002536/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL028481/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL30568/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK074317/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL079353/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL030568/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK072206/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K25 HL080079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007789/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- 1K25HL080079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 5F32DK074317/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL079353/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 ES045530/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- DK072206/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32-DK07789/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
