P63 (CKAP4) as an SP-A receptor: implications for surfactant turnover
- PMID: 20054143
- PMCID: PMC3025887
- DOI: 10.1159/000272062
P63 (CKAP4) as an SP-A receptor: implications for surfactant turnover
Abstract
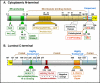
Surfactant protein-A (SP-A) plays an important role in the clearance of surfactant from the lung alveolar space and in the regulation of surfactant secretion and uptake by type II pneumocytes in culture. Two pathways are important for the endocytosis of surfactant by type II cells and the intact lung, a receptor-mediated clathrin-dependent pathway and a non-clathrin, actin-mediated pathway. The critical role of the clathrin/receptor-mediated pathway in normal mice is supported by the finding that SP-A gene-targeted mice use the actin-dependent pathway to maintain normal clearance of surfactant. Addition of SP-A to the surfactant of the SP-A null mice "rescued" the phenotype, further emphasizing the essential role of the SP-A/receptor-mediated process in surfactant turnover. This review presents an overview of the structure of SP-A and its function in surfactant turnover. The evidence that the interaction of SP-A with type II cells is a receptor-mediated process is presented. A newly identified receptor for SP-A, P63/CKAP4, is described in detail, with elucidation of the specific structural features of this 63 kDa, nonglycosylated, highly coiled, transmembrane protein. The compelling evidence that P63 functions as a receptor for SP-A on type II cells is summarized. Regulation of P63 receptor density on the surface of pneumocytes may be a novel approach for the regulation of surfactant homeostasis by the lung.
2010 S. Karger AG, Basel
Figures


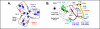



References
-
- Fisher AB. Lung Surfactant Clearance and Cellular Processing. In: Rooney SA, Landes RG, editors. Lung surfactant: cellular and molecular processing Medical Intelligence Unit 5. Austin, TX: Landes Bioscience; 1998. pp. 165–189.
-
- Khubchandani KR, Snyder JM. Surfactant protein A (SP-A): the alveolus and beyond. Faseb J. 2001;15:59–69. - PubMed
-
- Kuroki Y, Mason RJ, Voelker DR. Chemical modification of surfactant protein A alters high affinity binding to rat alveolar type II cells and regulation of phospholipid secretion. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:17596–17602. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
