Influence of calcium and vitamin D supplementation on weight and fat loss in obese women
- PMID: 20054189
- PMCID: PMC6515890
- DOI: 10.1159/000169831
Influence of calcium and vitamin D supplementation on weight and fat loss in obese women
Abstract
Background: Dairy products not only reduce the risk of hypertension and cardiovascular diseases but may play a role in the treatment of obesity. As there is some evidence that calcium (Ca) and vitamin D may play a role in effective weight management, we decided to evaluate the influence of Ca and vitamin D supplementation on weight and fat loss in obese women.
Material and methods: Forty obese women were enrolled in this study. Subjects were divided into 2 groups comparable with body mass index (BMI) and age. Group 1 was provided with calcium carbonate and 1-(OH)-vitamin D supplementation. Group 2 was provided with only a diet. Subjects participated in a 3-month weight reduction therapy (balanced diet, modification of life style, and regular physical exercise). Blood samples (serum concentration of Ca, phosphorus (P), parathormone (PTH), 25-(OH)-D3) and clinical characteristics (weight, height, BMI, body composition) were taken at baseline and after the 3-month program.
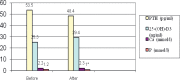
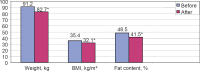
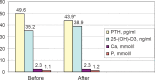
Results: No significant differences of body weight, body fat content, serum parathormone, 25-(OH)-D3 concentration, and plasma total Ca and P concentration were observed between analyzed groups both before and after the treatment. Additionally, we did not observe any significant influence of Ca and vitamin D supplementation on weight and fat loss.
Conclusion: Ca plus vitamin D supplementation during a 3-month low caloric diet has no additional effect on weight and fat loss in obese women.
Figures

References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System Survey Data Atlanta, GA, Dept of Health and Human Services CDC. 2000
-
- Appel LJ, Moore TJ, Obarzanek E, et al. A clinical trial of the effects of dietary patterns on blood pressure DASH Collaborative Research Group. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:1117–1124. - PubMed
-
- McCarron DA, Reusser ME. Finding consensus in the dietary calcium-blood pressure debate. J Am Coll Nutr. 1999;18:398–405. - PubMed
-
- Zemel MB. Calcium modulation of hypertension and obesity: mechanisms and implications. Am Coll Nutr. 2001;20:428–435. - PubMed
-
- Zemel MB, Shi H, Greer B, et al. Regulation of adiposity by dietary calcium. FASEB J. 2000;14:1132–1138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

