Hypothalamic lipids and the regulation of energy homeostasis
- PMID: 20054216
- PMCID: PMC6444804
- DOI: 10.1159/000209251
Hypothalamic lipids and the regulation of energy homeostasis
Abstract
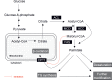
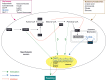
The hypothalamus is a specialised area in the brain that integrates the control of energy homeostasis, regulating both food intake and energy expenditure. The classical theory for hypothalamic feeding control is mainly based on the relationship between peripheral signals and neurotransmitters/neuromodulators in the central nervous system. Thus, hypothalamic neurons respond to peripheral signals, such as hormones and nutrients, by modifying the synthesis of neuropeptides. Despite the well-established role of these hypothalamic networks, increasing evidence indicates that the modulation of lipid metabolism in the hypothalamus plays a critical role in feeding control. In fact, the pharmacologic and genetic targeting of key enzymes from these pathways, such as AMP-activated protein kinase, acetyl-CoA carboxylase, carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1, fatty acid synthase, and malonyl-CoA decarboxylase, has a profound effect on food intake and body weight. Here, we review what is currently known about the relationship between hypothalamic lipid metabolism and whole body energy homeostasis. Defining these novel mechanisms may offer new therapeutic targets for the treatment of obesity and its associated pathologies.
2009 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Brain lipogenesis and regulation of energy metabolism.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2008 Jul;11(4):483-90. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e328302f3d8. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2008. PMID: 18542011 Review.
-
Regulation of food intake and energy expenditure by hypothalamic malonyl-CoA.Int J Obes (Lond). 2008 Sep;32 Suppl 4:S49-54. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2008.123. Int J Obes (Lond). 2008. PMID: 18719599 Review.
-
The role of hypothalamic malonyl-CoA in energy homeostasis.J Biol Chem. 2006 Dec 8;281(49):37265-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R600016200. Epub 2006 Oct 3. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 17018521 Review.
-
Role of lipids in the control of food intake.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2011 Mar;14(2):138-44. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0b013e3283437b78. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2011. PMID: 21252653 Review.
-
Targeting intermediary metabolism in the hypothalamus as a mechanism to regulate appetite.Pharmacol Rev. 2010 Jun;62(2):237-64. doi: 10.1124/pr.109.002428. Epub 2010 Apr 14. Pharmacol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20392806 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypothalamic inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase stimulates hepatic counter-regulatory response independent of AMPK activation in rats.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 23;8(4):e62669. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062669. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. Retraction in: PLoS One. 2023 Nov 27;18(11):e0295063. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295063. PMID: 23626844 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Leptin Receptors in RIP-Cre25Mgn Neurons Mediate Anti-dyslipidemia Effects of Leptin in Insulin-Deficient Mice.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Sep 23;11:588447. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.588447. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 33071988 Free PMC article.
-
CPT1A in AgRP neurons is required for sex-dependent regulation of feeding and thirst.Biol Sex Differ. 2023 Mar 25;14(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s13293-023-00498-8. Biol Sex Differ. 2023. PMID: 36966335 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of central obesity-related variants in LYPLAL1, NRXN3, MSRA, and TFAP2B on quantitative metabolic traits in adult Danes.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e20640. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020640. Epub 2011 Jun 2. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21674055 Free PMC article.
-
Nutrient Sensing Systems in Fish: Impact on Food Intake Regulation and Energy Homeostasis.Front Neurosci. 2017 Jan 5;10:603. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00603. eCollection 2016. Front Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28111540 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Frühbeck G, Gomez-Ambrosi J. Control of body weight: a physiologic and transgenic perspective. Diabetologia. 2003;46:143–172. - PubMed
-
- Medina-Gomez G, Vidal-Puig A. Gateway to the metabolic syndrome. Nat Med. 2005;11:602–603. - PubMed
-
- Farooqi IS, O'Rahilly S. Monogenic obesity in humans. Annu Rev Med. 2005;56:443–458. - PubMed
-
- Slawik M, Vidal-Puig AJ. Lipotoxicity, overnutrition and energy metabolism in aging. Ageing Res Rev. 2006;5:144–164. - PubMed
-
- Hecherington A, Ranson S. The spontaneous activity and food intake of rats with hypothalamic lesions. Am J Physiol. 1942;136:609–617.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

