Evolution and origin of HRS, a protein interacting with Merlin, the Neurofibromatosis 2 gene product
- PMID: 20054405
- PMCID: PMC2796970
- DOI: 10.4137/grsb.s3106
Evolution and origin of HRS, a protein interacting with Merlin, the Neurofibromatosis 2 gene product
Abstract
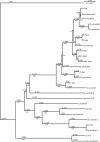
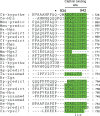
Hepatocyte growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase substrate (HRS) is an endosomal protein required for trafficking receptor tyrosine kinases from the early endosome to the lysosome. HRS interacts with Merlin, the Neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2) gene product, and this interaction may be important for Merlin's tumor suppressor activity. Understanding the evolution, origin, and structure of HRS may provide new insight into Merlin function. We show that HRS homologs are present across a wide range of Metazoa with the yeast Vps27 protein as their most distant ancestor. The phylogenetic tree of the HRS family coincides with species evolution and divergence, suggesting a unique function for HRS. Sequence alignment shows that various protein domains of HRS, including the VHS domain, the FYVE domain, the UIM domain, and the clathrin-binding domain, are conserved from yeast to multicellular organisms. The evolutionary transition from unicellular to multicellular organisms was accompanied by the appearance of a binding site for Merlin, which emerges in the early Metazoa after its separation from flatworms. In addition to the region responsible for growth suppression, the Merlin-binding and STAM-binding domains of HRS are conserved among multicellular organisms. The residue equivalent to tyrosine-377, which is phosphorylated in the human HRS protein, is highly conserved throughout the HRS family. Three additional conserved boxes lacking assigned functions are found in the HRS proteins of Metazoa. While boxes 1 and 3 may constitute the Eps-15-and Snx1-binding sites, respectively, box 2, containing the residue equivalent to tyrosine-377, is likely to be important for HRS phosphorylation. While several functional domains are conserved throughout the HRS family, the STAM-binding, Merlin-binding, and growth suppression domains evolved in the early Metazoa around the time the Merlin protein emerged. As these domains appear during the transition to multicellularity, their functional roles may be related to cell-cell interaction.
Keywords: HRS; Merlin; endosomal protein; hepatocyte growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase substrate.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Evolution and origin of merlin, the product of the Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) tumor-suppressor gene.BMC Evol Biol. 2005 Dec 2;5:69. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-5-69. BMC Evol Biol. 2005. PMID: 16324214 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of the relationship between the neurofibromatosis 2 tumor suppressor and its binding partner, hepatocyte growth factor-regulated tyrosine kinase substrate.Hum Mol Genet. 2002 Dec 1;11(25):3167-78. doi: 10.1093/hmg/11.25.3167. Hum Mol Genet. 2002. PMID: 12444101
-
The NF2 interactor, hepatocyte growth factor-regulated tyrosine kinase substrate (HRS), associates with merlin in the "open" conformation and suppresses cell growth and motility.Hum Mol Genet. 2001 Apr 1;10(8):825-34. doi: 10.1093/hmg/10.8.825. Hum Mol Genet. 2001. PMID: 11285248
-
The merlin interacting proteins reveal multiple targets for NF2 therapy.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Jan;1785(1):32-54. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2007.10.001. Epub 2007 Oct 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 17980164 Review.
-
Merlin: the neurofibromatosis 2 tumor suppressor.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999 Mar 25;1423(2):M29-36. doi: 10.1016/s0304-419x(99)00005-0. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999. PMID: 10214350 Review.
Cited by
-
Emergence and Evolution of ERM Proteins and Merlin in Metazoans.Genome Biol Evol. 2020 Jan 1;12(1):3710-3724. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evz265. Genome Biol Evol. 2020. PMID: 31851361 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asao H, Sasaki Y, Arita T, et al. HRS is associated with STAM, a signal-transducing adaptor molecule. Its suppressive effect on cytokine-induced cell growth. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:32785–91. - PubMed
-
- Komada M, Masaki R, Yamamoto A, Kitamura N. HRS, a tyrosine kinase substrate with a conserved double zinc finger domain, is localized to the cytoplasmic surface of early endosomes. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:20538–44. - PubMed
-
- Seto ES, Bellen HJ, Lloyd TE. When cell biology meets development: endocytic regulation of signaling pathways. Genes Dev. 2002;16:1314–36. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

