Nanomedicine in pulmonary delivery
- PMID: 20054434
- PMCID: PMC2802043
- DOI: 10.2147/ijn.s4937
Nanomedicine in pulmonary delivery
Abstract
The lung is an attractive target for drug delivery due to noninvasive administration via inhalation aerosols, avoidance of first-pass metabolism, direct delivery to the site of action for the treatment of respiratory diseases, and the availability of a huge surface area for local drug action and systemic absorption of drug. Colloidal carriers (ie, nanocarrier systems) in pulmonary drug delivery offer many advantages such as the potential to achieve relatively uniform distribution of drug dose among the alveoli, achievement of improved solubility of the drug from its own aqueous solubility, a sustained drug release which consequently reduces dosing frequency, improves patient compliance, decreases incidence of side effects, and the potential of drug internalization by cells. This review focuses on the current status and explores the potential of colloidal carriers (ie, nanocarrier systems) in pulmonary drug delivery with special attention to their pharmaceutical aspects. Manufacturing processes, in vitro/in vivo evaluation methods, and regulatory/toxicity issues of nanomedicines in pulmonary delivery are also discussed.
Keywords: colloidal carriers; dendrimer; liposome; nanocarrier systems; polymeric nanoparticle; pulmonary delivery; solid lipid nanoparticle; submicron emulsion.
Figures


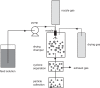
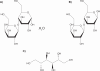
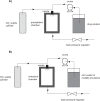
References
-
- Yang W, Peters JI, Williams RO., 3rd Inhaled nanoparticles–a current review. Int J Pharm. 2008;356:239–247. - PubMed
-
- Patton JS, Byron PR. Inhaling medicines: delivering drugs to the body through the lungs. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6:67–74. - PubMed
-
- Sung JC, Pulliam BL, Edwards DA. Nanoparticles for drug delivery to the lungs. Trends Biotechnol. 2007;25:563–570. - PubMed
-
- Bailey MM, Berkland CJ. Nanoparticle formulations in pulmonary drug delivery. Med Res Rev. 2009;29:196–212. - PubMed
-
- Shekunov B. Nanoparticle technology for drug delivery – From nanoparticles to cutting-edge delivery strategies – Part I – 21–22 March 2005, Philadelphia, PA, USA. Idrugs. 2005;8:399–401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

