Case report: calcific tendinitis of the rectus femoris: a rare cause of snapping hip
- PMID: 20054675
- PMCID: PMC3049605
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-009-1208-9
Case report: calcific tendinitis of the rectus femoris: a rare cause of snapping hip
Abstract
Background: Internal snapping hip is a syndrome caused by recurrent subluxation of the iliopsoas tendon. There is little agreement regarding the impinging sites responsible for the jerky motion of the tendon. Thus far, the lesser trochanter, anterior capsule, and iliopectineal eminence are considered the most likely catching sites.
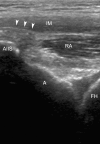
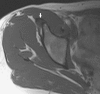
Case description: We report an unusual case in which a calcific tendinitis of the rectus femoris direct head impinged against the overlying iliacus muscle, resulting in a painful coxa saltans. The exclusive involvement of the direct head hid the calcium deposit on standard radiographs, whereas MRI suggested but poorly showed the tendon disease. Dynamic ultrasonography and CT scanning allowed a precise diagnosis and subsequent treatment with CT-guided steroid injection.
Literature review: Calcific tendinitis of the rectus anterior direct head has not been reported as a possible cause of snapping hip; involvement of the direct head in rectus anterior calcific tendinitis was described in one case.
Purposes and clinical relevance: Our case shows the rectus anterior direct head may be involved in the etiology of coxa saltans. Theoretically any thickening of the tendon might activate the same pathomechanism. Physicians should consider this possible new cause of internal snapping hip when the most common ones have been excluded, especially as it may be managed easily with steroid injection.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

