Dystroglycan is not required for maintenance of the luminal epithelial basement membrane or cell polarity in the mouse prostate
- PMID: 20054819
- PMCID: PMC2857647
- DOI: 10.1002/pros.21110
Dystroglycan is not required for maintenance of the luminal epithelial basement membrane or cell polarity in the mouse prostate
Abstract
Background: Dystroglycan is a cell-surface receptor for extracellular matrix proteins including laminins and perlecan. Prior studies have shown its involvement in assembly and/or maintenance of basement membrane structures, cell polarity and tissue morphogenesis; and its expression is often reduced in prostate and other cancers. However, the role of dystroglycan in normal epithelial tissues such as the prostate is unclear.
Methods: To investigate this, we disrupted dystroglycan expression in the prostate via a conditional gene targeting strategy utilizing Cre recombinase expressed in luminal prostate epithelial cells.
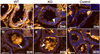
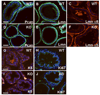
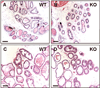
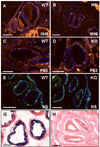
Results: Contrary to expectations, deletion of dystroglycan in luminal epithelial cells resulted in no discernable phenotype as judged by histology, basement membrane ultrastructure, localization of dystroglycan ligands, cell polarity or regenerative capacity of the prostate following castration. Dystroglycan expression remains in keratin-5-positive basal cells located in the proximal ducts where dystroglycan expression is elevated in regenerating prostates.
Conclusions: Our results show that dystroglycan in luminal epithelial cells is not required for the maintenance of basement membranes, cell polarity or prostate regeneration. However, it is possible that persistent dystroglycan expression in the basal cell compartment may support these or other functions.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dystroglycan and perlecan provide a basal cue required for epithelial polarity during energetic stress.Dev Cell. 2009 Jan;16(1):83-92. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2008.11.006. Dev Cell. 2009. Retraction in: Dev Cell. 2013 Oct 28;27(2):241. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2013.09.019. PMID: 19154720 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Distribution of dystroglycan in normal adult mouse tissues.J Histochem Cytochem. 1998 Apr;46(4):449-57. doi: 10.1177/002215549804600404. J Histochem Cytochem. 1998. PMID: 9524190
-
Integrin and dystroglycan compensate each other to mediate laminin-dependent basement membrane assembly and epiblast polarization.Matrix Biol. 2017 Jan;57-58:272-284. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2016.07.005. Epub 2016 Jul 20. Matrix Biol. 2017. PMID: 27449702 Free PMC article.
-
Non-integrin laminin receptors in epithelia.Tissue Cell. 2019 Feb;56:71-78. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2018.12.005. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Tissue Cell. 2019. PMID: 30736907 Review.
-
Receptors for laminins during epithelial morphogenesis.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996 Oct;8(5):700-6. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(96)80112-8. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8939658 Review.
Cited by
-
Loss of LARGE2 disrupts functional glycosylation of α-dystroglycan in prostate cancer.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jan 25;288(4):2132-42. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.432807. Epub 2012 Dec 6. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23223448 Free PMC article.
-
Integrins and epithelial cell polarity.J Cell Sci. 2014 Aug 1;127(Pt 15):3217-25. doi: 10.1242/jcs.146142. Epub 2014 Jul 2. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 24994933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The microstructure of laminin-111 compensates for dystroglycan loss in mammary epithelial cells in downstream expression of milk proteins.Biomaterials. 2019 Oct;218:119337. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119337. Epub 2019 Jul 9. Biomaterials. 2019. PMID: 31325803 Free PMC article.
-
Dystroglycan controls signaling of multiple hormones through modulation of STAT5 activity.J Cell Sci. 2010 Nov 1;123(Pt 21):3683-92. doi: 10.1242/jcs.070680. Epub 2010 Oct 12. J Cell Sci. 2010. PMID: 20940259 Free PMC article.
-
Slow disease progression in a C57BL/6 pten-deficient mouse model of prostate cancer.Am J Pathol. 2011 Jul;179(1):502-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.03.014. Epub 2011 May 7. Am J Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21703427 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ervasti JM, Ohlendieck K, Kahl SD, Gaver MG, Campbell KP. Deficiency of a glycoprotein component of the dystrophin complex in dystrophic muscle. Nature. 1990;345(6273):315–319. - PubMed
-
- Ervasti JM, Campbell KP. Membrane organization of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex. Cell. 1991;66(6):1121–1131. - PubMed
-
- Ibraghimov-Beskrovnaya O, Ervasti JM, Leveille CJ, Slaughter CA, Sernett SW, Campbell KP. Primary structure of dystrophin-associated glycoproteins linking dystrophin to the extracellular matrix. Nature. 1992;355(6362):696–702. - PubMed
-
- Jung D, Yang B, Meyer J, Chamberlain JS, Campbell KP. Identification and characterization of the dystrophin anchoring site on beta-dystroglycan. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(45):27305–27310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

