Extracellular beta-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (beta-NAD) promotes the endothelial cell barrier integrity via PKA- and EPAC1/Rac1-dependent actin cytoskeleton rearrangement
- PMID: 20054824
- PMCID: PMC2893378
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.22029
Extracellular beta-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (beta-NAD) promotes the endothelial cell barrier integrity via PKA- and EPAC1/Rac1-dependent actin cytoskeleton rearrangement
Abstract
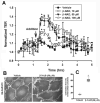
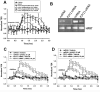
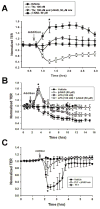
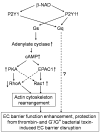
Extracellular beta-NAD is known to elevate intracellular levels of calcium ions, inositol 1,4,5-trisphate and cAMP. Recently, beta-NAD was identified as an agonist for P2Y1 and P2Y11 purinergic receptors. Since beta-NAD can be released extracellularly from endothelial cells (EC), we have proposed its involvement in the regulation of EC permeability. Here we show, for the first time, that endothelial integrity can be enhanced in EC endogenously expressing beta-NAD-activated purinergic receptors upon beta-NAD stimulation. Our data demonstrate that extracellular beta-NAD increases the transendothelial electrical resistance (TER) of human pulmonary artery EC (HPAEC) monolayers in a concentration-dependent manner indicating endothelial barrier enhancement. Importantly, beta-NAD significantly attenuated thrombin-induced EC permeability as well as the barrier-compromising effects of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial toxins representing the barrier-protective function of beta-NAD. Immunofluorescence microscopy reveals more pronounced staining of cell-cell junctional protein VE-cadherin at the cellular periphery signifying increased tightness of the cell-cell contacts after beta-NAD stimulation. Interestingly, inhibitory analysis (pharmacological antagonists and receptor sequence specific siRNAs) indicates the participation of both P2Y1 and P2Y11 receptors in beta-NAD-induced TER increase. beta-NAD-treatment attenuates the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced phosphorylation of myosin light chain (MLC) indicating its involvement in barrier protection. Our studies also show the involvement of cAMP-dependent protein kinase A and EPAC1 pathways as well as small GTPase Rac1 in beta-NAD-induced EC barrier enhancement. With these results, we conclude that beta-NAD regulates the pulmonary EC barrier integrity via small GTPase Rac1- and MLCP- dependent signaling pathways.
Keywords: EPAC1; Gq protein; Gs protein; HPAEC; P2Y antagonists; P2Y1 and P2Y11 receptors; Rac1; cAMP.
J. Cell. Physiol. 223: 215-223, 2010. (c) 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Exendin-4 promotes endothelial barrier enhancement via PKA- and Epac1-dependent Rac1 activation.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015 Jan 15;308(2):C164-75. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00249.2014. Epub 2014 Nov 5. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25377089
-
Prostaglandins PGE(2) and PGI(2) promote endothelial barrier enhancement via PKA- and Epac1/Rap1-dependent Rac activation.Exp Cell Res. 2007 Jul 1;313(11):2504-20. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.03.036. Epub 2007 Apr 6. Exp Cell Res. 2007. PMID: 17493609 Free PMC article.
-
Differential mechanisms of adenosine- and ATPγS-induced microvascular endothelial barrier strengthening.J Cell Physiol. 2019 May;234(5):5863-5879. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26419. Epub 2018 Dec 17. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 29271489 Free PMC article.
-
Cross talk between focal adhesion kinase and cadherins: role in regulating endothelial barrier function.Microvasc Res. 2012 Jan;83(1):3-11. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2011.08.001. Epub 2011 Aug 16. Microvasc Res. 2012. PMID: 21864544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions between Epac1 and ezrin in the control of endothelial barrier function.Biochem Soc Trans. 2014 Apr;42(2):274-8. doi: 10.1042/BST20130271. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014. PMID: 24646230 Review.
Cited by
-
Impaired pulmonary endothelial barrier function in sickle cell mice.Haematologica. 2017 Jan;102(1):e26-e29. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2016.153098. Epub 2016 Sep 29. Haematologica. 2017. PMID: 27686374 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Agonist of growth hormone-releasing hormone reduces pneumolysin-induced pulmonary permeability edema.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Feb 7;109(6):2084-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1121075109. Epub 2012 Jan 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22308467 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular adenosine-induced Rac1 activation in pulmonary endothelium: Molecular mechanisms and barrier-protective role.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Aug;233(8):5736-5746. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26281. Epub 2018 Mar 7. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29168172 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 regulates matrix metalloproteinase-2-mediated endothelial barrier dysfunction and breast cancer cell transmigration through lung microvascular endothelial cells.Mol Cancer Res. 2010 Jul;8(7):939-51. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0523. Epub 2010 Jun 22. Mol Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20571065 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mediated Angiogenesis and Vasculogenesis Networks.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 30;26(13):6316. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136316. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650092 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baffert F, Le T, Thurston G, McDonald DM. Angiopoietin-1 decreases plasma leakage by reducing number and size of endothelial gaps in venules. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006;290(1):H107–118. - PubMed
-
- Bai JW, Deng WW, Zhang J, Xu SM, Zhang DX. [Protective effect of myosin light-chain kinase inhibitor on acute lung injury] Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2009;21(4):215–218. - PubMed
-
- Birukova AA, Smurova K, Birukov KG, Kaibuchi K, Garcia JG, Verin AD. Role of Rho GTPases in thrombin-induced lung vascular endothelial cells barrier dysfunction. Microvasc Res. 2004a;67(1):64–77. - PubMed
-
- Birukova AA, Smurova K, Birukov KG, Usatyuk P, Liu F, Kaibuchi K, Ricks-Cord A, Natarajan V, Alieva I, Garcia JG, Verin AD. Microtubule disassembly induces cytoskeletal remodeling and lung vascular barrier dysfunction: role of Rho-dependent mechanisms. J Cell Physiol. 2004b;201(1):55–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

