Novel peptoid building blocks: synthesis of functionalized aromatic helix-inducing submonomers
- PMID: 20055478
- PMCID: PMC2814525
- DOI: 10.1021/ol902660p
Novel peptoid building blocks: synthesis of functionalized aromatic helix-inducing submonomers
Abstract
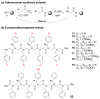
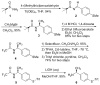
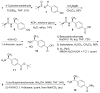
Peptoids, oligo-N-substituted glycines, can fold into well-defined helical secondary structures. The design and synthesis of new peptoid building blocks that are capable of both (a) inducing a helical secondary structure and (b) decorating the helices with chemical functionalities are reported. Peptoid heptamers containing carboxamide, carboxylic acid or thiol functionalities were synthesized, and the resulting peptoids were shown to form stable helices. A thiol-containing peptoid readily formed the homodisulfide, providing a convenient route to prepare peptoid helix homodimers.
Figures


References
-
- Branden C, Tooze J. Introduction to Protein Structure. 2nd. Garland Publishing Inc.; New York, NY: 1999.
-
- Barron AE, Zuckermann RN. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 1999;3:681–687. - PubMed
-
- Simons RJ, Kania RS, Zuckermann RN, Huebner VD, Jewell DA, Banville S, Ng S, Wang L, Rosenberg S, Marlowe CK, Spellmeyer DC, Tan R, Frankel AD, Santi DV, Cohen FE, Bartlett PA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89:9367–9371. - PMC - PubMed
- Fowler SA, Blackwell HE. Org Biomol Chem. 2009;7:1508–1524. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zuckermann RN, Kerr JM, Kent SBH, Moos WH. J Am Chem Soc. 1992;114:10646–10647.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

