Molecular mechanisms of system control of NF-kappaB signaling by IkappaBalpha
- PMID: 20055496
- PMCID: PMC2865148
- DOI: 10.1021/bi901948j
Molecular mechanisms of system control of NF-kappaB signaling by IkappaBalpha
Abstract
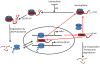
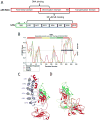
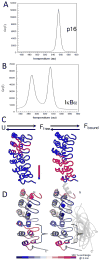
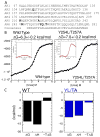
The NF-kappaB family of transcription factors responds to inflammatory cytokines with rapid transcriptional activation and subsequent signal repression. Much of the system control depends on the unique characteristics of its major inhibitor, IkappaBalpha, which appears to have folding dynamics that underlie the biophysical properties of its activity. Theoretical folding studies followed by experiments have shown that a portion of the ankyrin repeat domain of IkappaBalpha folds on binding. In resting cells, IkappaBalpha is constantly being synthesized, but most of it is rapidly degraded, leaving only a very small pool of free IkappaBalpha. Nearly all of the NF-kappaB is bound to IkappaBalpha, resulting in near-complete inhibition of nuclear localization and transcriptional activation. Combined solution biophysical measurements and quantitative protein half-life measurements inside cells have allowed us to understand how the inhibition occurs, why IkappaBalpha can be degraded quickly in the free state but remain extremely stable in the bound state, and how signal activation and repression can be tuned by IkappaB folding dynamics. This review summarizes results of in vitro and in vivo experiments that converge demonstrating the effective interplay between biophysics and cell biology in understanding transcriptional control by the NF-kappaB signaling module.
Figures
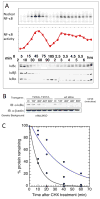
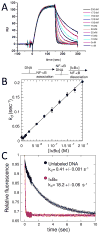
Similar articles
-
Pre-folding IkappaBalpha alters control of NF-kappaB signaling.J Mol Biol. 2008 Jun 27;380(1):67-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.02.053. Epub 2008 Mar 4. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18511071 Free PMC article.
-
Consequences of fuzziness in the NFκB/IκBα interaction.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;725:74-85. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-0659-4_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22399319 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of a ternary complex of NF-kappaB and IkappaBalpha with DNA provides insights into how IkappaBalpha removes NF-kappaB from transcription sites.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jan 25;108(4):1367-72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014323108. Epub 2011 Jan 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21220295 Free PMC article.
-
Regions of IkappaBalpha that are critical for its inhibition of NF-kappaB.DNA interaction fold upon binding to NF-kappaB.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Dec 12;103(50):18951-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605794103. Epub 2006 Dec 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17148610 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of IkappaBalpha function and NF-kappaB signaling: AEBP1 is a novel proinflammatory mediator in macrophages.Mediators Inflamm. 2010;2010:823821. doi: 10.1155/2010/823821. Epub 2010 Apr 12. Mediators Inflamm. 2010. PMID: 20396415 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
How the ankyrin and SOCS box protein, ASB9, binds to creatine kinase.Biochemistry. 2015 Mar 3;54(8):1673-80. doi: 10.1021/bi501420n. Epub 2015 Feb 17. Biochemistry. 2015. PMID: 25654263 Free PMC article.
-
Monocytic-Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells of HIV-Infected Individuals With Viral Suppression Exhibit Suppressed Innate Immunity to Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 28;12:647019. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.647019. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33995365 Free PMC article.
-
Visualization of the nanospring dynamics of the IkappaBalpha ankyrin repeat domain in real time.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jun 21;108(25):10178-83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102226108. Epub 2011 May 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21628581 Free PMC article.
-
Aldose reductase participates in the downregulation of T cell functions due to suppressor macrophages.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 12;6:21093. doi: 10.1038/srep21093. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26868163 Free PMC article.
-
Protein phosphatases in TLR signaling.Cell Commun Signal. 2021 Apr 21;19(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s12964-021-00722-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2021. PMID: 33882943 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hoffmann A, Levchenko A, Scott ML, Baltimore D. The IkappaB-NF-kappaB signaling module: temporal control and selective gene activation. Science. 2002;298:1241–1245. - PubMed
-
- Ghosh S, May MJ, Kopp EB. NF-kappa B and Rel proteins: evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:225–260. - PubMed
-
- Kumar A, Takada Y, Boriek AM, Aggarwal BB. Nuclear factor-kappaB: its role in health and disease. J Mol Med. 2004;82:434–448. - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann A, Baltimore D. Circuitry of nuclear factor kappaB signaling. Immunol Rev. 2006;210:171–186. - PubMed
-
- Verma IM, Stevenson JK, Schwarz EM, Van Antwerp D, Miyamoto S. Rel/NF-kappa B/I kappa B family: intimate tales of association and dissociation. Genes Dev. 1995;9:2723–2735. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

