Functional motifs in biochemical reaction networks
- PMID: 20055671
- PMCID: PMC3773234
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.physchem.012809.103457
Functional motifs in biochemical reaction networks
Abstract
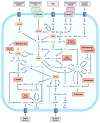
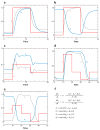
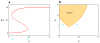
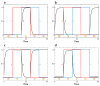
The signal-response characteristics of a living cell are determined by complex networks of interacting genes, proteins, and metabolites. Understanding how cells respond to specific challenges, how these responses are contravened in diseased cells, and how to intervene pharmacologically in the decision-making processes of cells requires an accurate theory of the information-processing capabilities of macromolecular regulatory networks. Adopting an engineer's approach to control systems, we ask whether realistic cellular control networks can be decomposed into simple regulatory motifs that carry out specific functions in a cell. We show that such functional motifs exist and review the experimental evidence that they control cellular responses as expected.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Simplified models of biological networks.Annu Rev Biophys. 2010;39:43-59. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.093008.131241. Annu Rev Biophys. 2010. PMID: 20192769 Review.
-
A method for inverse bifurcation of biochemical switches: inferring parameters from dose response curves.BMC Syst Biol. 2014 Nov 20;8:114. doi: 10.1186/s12918-014-0114-2. BMC Syst Biol. 2014. PMID: 25409687 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress on the analysis of power-law features in complex cellular networks.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2007;49(1):37-47. doi: 10.1007/s12013-007-0040-7. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2007. PMID: 17873338 Review.
-
Simple molecular networks that respond optimally to time-periodic stimulation.BMC Syst Biol. 2009 Mar 3;3:29. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-3-29. BMC Syst Biol. 2009. PMID: 19257878 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the organization of biochemical regulatory networks using graph theory analyses.J Biol Chem. 2009 Feb 27;284(9):5451-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R800056200. Epub 2008 Oct 20. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 18940806 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding virtual patients efficiently and rigorously by combining machine learning with dynamical modelling.J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2022 Feb;49(1):117-131. doi: 10.1007/s10928-021-09798-1. Epub 2022 Jan 5. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2022. PMID: 34985622 Free PMC article.
-
Role for regulated phosphatase activity in generating mitotic oscillations in Xenopus cell-free extracts.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Dec 17;110(51):20539-44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1318065110. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24297885 Free PMC article.
-
Rule-based modeling: a computational approach for studying biomolecular site dynamics in cell signaling systems.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2014 Jan-Feb;6(1):13-36. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1245. Epub 2013 Sep 30. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 24123887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design principles of regulatory networks: searching for the molecular algorithms of the cell.Mol Cell. 2013 Jan 24;49(2):202-12. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.12.020. Mol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23352241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamical scenarios for chromosome bi-orientation.Biophys J. 2013 Jun 18;104(12):2595-606. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.05.005. Biophys J. 2013. PMID: 23790367 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray D. Protein molecules as computational elements in living cells. Nature. 1995;376:307–12. - PubMed
-
- Alon U. Network motifs: theory and experimental approaches. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:450–61. - PubMed
-
- Alon U. An Introduction to Systems Biology: Design Principles of Biological Circuits. Boca Raton, FL: Chapman & Hall/CRC; 2007.
-
- Thomas R, D’Ari R. Biological Feedback. Boca Raton, FL: CRC; 1990.
-
- Wolf DM, Arkin AP. Motifs, modules and games in bacteria. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2003;6:125–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

