Vascular KCa-channels as therapeutic targets in hypertension and restenosis disease
- PMID: 20055714
- PMCID: PMC3644209
- DOI: 10.1517/14728220903540257
Vascular KCa-channels as therapeutic targets in hypertension and restenosis disease
Abstract
Importance of the field: Cardiovascular disease is a leading cause of death in modern societies. Hyperpolarizing Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels (K(Ca)) are important membrane proteins in the control of arterial tone and pathological vascular remodelling and thus could serve as new drug targets.
Areas covered in this review: We summarize recent advances in the field of vascular K(Ca) and their roles in cardiovascular pathologies such as hypertension and restenosis disease and draw attention to novel small-molecule channel modulators and their possible therapeutic utility. This review focuses on literature from the last four to five years.
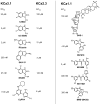
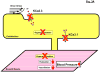
What the reader will gain: Pharmacological opening of endothelial KCa3.1/KCa2.3 channels stimulates endothelium-derived-hyperpolarizing-factor-mediated arteriolar dilation and lowers blood pressure. Inhibition of smooth muscle KCa3.1 channels has beneficial effects in restenosis disease and atherosclerosis. We consider the therapeutic potential of KCa3.1/KCa2.3 openers as novel endothelium-specific antihypertensive drugs as well as of KCa3.1-blockers for the treatment of pathological vascular remodelling and discuss advantages and disadvantages of the pharmacotherapeutic approaches.
Take home message: Pharmacological manipulation of vascular K(Ca) channels by novel small-molecule modulators offers new venues for alternative treatments of hypertension, restenosis and atherosclerosis. Additional efforts are required to optimize these compounds and to validate them as cardiovascular-protective drugs.
Figures


References
-
- Endemann DH, Schiffrin EL. Endothelial dysfunction. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15:1983–92. - PubMed
-
- Spieker LE, Flammer AJ, Luscher TF. The vascular endothelium in hypertension. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2006:249–83. - PubMed
-
- Feletou M, Vanhoutte PM. Endothelial dysfunction: a multifaceted disorder (The Wiggers Award Lecture) Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006;291:H985–1002. - PubMed
-
- Zargham R. Preventing restenosis after angioplasty: a multistage approach. Clin Sci (Lond) 2008;114:257–64. - PubMed
-
- Furchgott RF, Zawadzki JV. The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature. 1980;288:373–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
