Exogenous thymosin beta4 prevents apoptosis in human intervertebral annulus cells in vitro
- PMID: 20055734
- PMCID: PMC2886502
- DOI: 10.3109/10520290903116884
Exogenous thymosin beta4 prevents apoptosis in human intervertebral annulus cells in vitro
Abstract
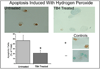
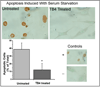
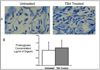
Loss of cells in the human disc due to programmed cell death (apoptosis) is a major factor in the aging and degenerating human intervertebral disc. Our objective here was to determine if thymosin beta(4) (TB4), a small, multifunctional 5 kDa protein with diverse activities, might block apoptosis in human annulus cells cultured in monolayer or three-dimensional (3D) culture. Apoptosis was induced in vitro using hydrogen peroxide or serum starvation. Annulus cells were processed for identification of apoptotic cells using the TUNEL method. The percentage of apoptotic cells was determined by cell counts. Annulus cells also were treated with TB4 for determination of proliferation, and proteoglycan production was assessed using cell titer and 1,2 dimethylmethylamine (DMB) assays and histological staining. A significant reduction in disc cell apoptosis occurred after TB4 treatment. The percentage of cells undergoing apoptosis decreased significantly in TB4 treated cells in both apoptosis induction designs. TB4 exposure did not alter proteoglycan production as assessed by either DMB measurement or histological staining. Our results indicate the need for further studies of the anti-apoptotic effect of TB4 and suggest that TB4 may have therapeutic application in future biological therapies for disc degeneration.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anti-apoptotic effects of IGF-1 and PDGF on human intervertebral disc cells in vitro.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000 Sep 1;25(17):2153-7. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200009010-00002. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000. PMID: 10973395
-
Deleterious effects of discography radiocontrast solution on human annulus cell in vitro: changes in cell viability, proliferation, and apoptosis in exposed cells.Spine J. 2012 Apr;12(4):329-35. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2012.02.003. Epub 2012 Mar 16. Spine J. 2012. PMID: 22424848
-
Effect of hyperbaric oxygenation on intervertebral disc degeneration: an in vitro study with human lumbar nucleus pulposus.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011 Nov 1;36(23):1925-31. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181feebde. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011. PMID: 21289555
-
Changes with age in proteoglycan synthesis in cells cultured in vitro from the inner and outer rabbit annulus fibrosus. Responses to interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist protein.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000 Jan 15;25(2):166-9. doi: 10.1097/00007632-200001150-00005. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000. PMID: 10685479
-
Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells from the sand rat: transforming growth factor beta and 3D co-culture with human disc cells stimulate proteoglycan and collagen type I rich extracellular matrix.Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10(4):R89. doi: 10.1186/ar2473. Epub 2008 Aug 11. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008. PMID: 18691412 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Adjunctive Thymosin Beta-4 Treatment Influences PMN Effector Cell Function during Pseudomonas aeruginosa-Induced Corneal Infection.Cells. 2021 Dec 18;10(12):3579. doi: 10.3390/cells10123579. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34944086 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative transcriptional profiling of regenerating damaged knee joints in two animal models of the newt Notophthalmus viridescens strengthens the role of candidate genes involved in osteoarthritis.Osteoarthr Cartil Open. 2022 May 21;4(3):100273. doi: 10.1016/j.ocarto.2022.100273. eCollection 2022 Sep. Osteoarthr Cartil Open. 2022. PMID: 36474938 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-125b-1-3p mediates intervertebral disc degeneration in rats by targeting teashirt zinc finger homeobox 3.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Mar;15(3):2627-2633. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.5715. Epub 2018 Jan 8. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29456666 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNA Let-7i-5p-Contained Small Extracellular Vesicles from Macrophages Induce Nucleus Pulposus Cell Senescence via Targeting LIN28A.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Feb 18;20:2163-2179. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S482646. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 39990291 Free PMC article.
-
Thymosin β4 in rheumatoid arthritis: Friend or foe.Biomed Rep. 2017 Sep;7(3):205-208. doi: 10.3892/br.2017.952. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Biomed Rep. 2017. PMID: 28808568 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bock-Marquette I, Saxena A, White MD, Dimaio JM, Srivastava D. Thymosin beta4 activates integrin-linked kinase and promotes cardiac cell migration, survival and cardiac repair. Nature. 2004;432:466–472. - PubMed
-
- Bonnet D, Lemoine FM, Frobert Y, Bonnet ML, Baillou C, Najman A, Guigon M. Thymosin beta4, inhibitor for normal hematopoietic progenitor cells. Exp. Hematol. 1996;24:776–782. - PubMed
-
- Bubb MR. Thymosin beta 4 interactions. Vitam. Horm. 2003;66:297–316. - PubMed
-
- Choi SY, Kim DK, Eun B, Kim K, Sun W, Kim H. Anti-apoptotic function of thymosin-beta in developing chick spinal motor neurons. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006;346:872–878. - PubMed
-
- Choi SY, Noh MR, Kim DK, Sun W, Kim H. Neuroprotective function of thymosin-beta and its derivative peptides on the programmed cell death of chick and rat neurons. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007;362:587–593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
