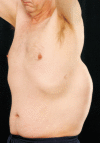
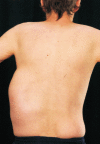
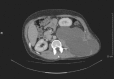
An extreme presentation of pancreatic pseudocyst
- PMID: 20056055
- PMCID: PMC5696823
- DOI: 10.1308/147870810X476683
An extreme presentation of pancreatic pseudocyst
Abstract
Pancreatitis is a serious and common presentation to general surgery departments. There are many complications associated with pancreatitis and we present an undescribed presentation of a pancreatic pseudocyst and include its management strategy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Pathogenesis and treatment of pancreatic pseudocyst and pancreatic fistula].Klin Khir. 1997;(1):23-4. Klin Khir. 1997. PMID: 9254260 Ukrainian.
-
[Pancreatic ascites].Rev Esp Enferm Apar Dig. 1985 Mar;67(3):275-9. Rev Esp Enferm Apar Dig. 1985. PMID: 4001521 Spanish. No abstract available.
-
Unusual presentation of a pancreatic pseudocyst: a case report.Can J Surg. 1987 Jul;30(4):281-2. Can J Surg. 1987. PMID: 3607643
-
Management of complications of pancreatitis.Curr Probl Surg. 1998 Jan;35(1):1-98. Curr Probl Surg. 1998. PMID: 9462408 Review. No abstract available.
-
[The treatment of a simple pancreatic pseudoaneurysm or one associated with hemosuccus pancreaticus].Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 1992 Mar;81(3):189-94. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 1992. PMID: 1567720 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Pancreatic pseudocyst with spontaneous cutaneous fistulization: Case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Aug;97(35):e12051. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012051. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30170417 Free PMC article.
-
Management of a Rapidly Progressing Huge Pancreatic Pseudocyst.Cureus. 2025 Feb 9;17(2):e78768. doi: 10.7759/cureus.78768. eCollection 2025 Feb. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40070604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lillemore KD, Yeo CJ. Management of complications of pancreatitis. Curr Problems Surg 1998; : 1–98. - PubMed
-
- Yeo CJ. Pancreatic pseudocysts, ascites and fistulas. Curr Opin Gen Surg 1994; 173–8. - PubMed
-
- Bradley EL. Complications of chronic pancreatitis. Surg Clin North Am 1989; : 481–97. - PubMed
-
- Adams DB, Harvey TS, Anderson MC. Percutaneous catheter drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts. Am Surg 1991; : 29–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical