Neuronostatin is co-expressed with somatostatin and mobilizes calcium in cultured rat hypothalamic neurons
- PMID: 20056135
- PMCID: PMC2824007
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.12.059
Neuronostatin is co-expressed with somatostatin and mobilizes calcium in cultured rat hypothalamic neurons
Abstract
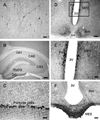
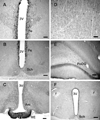
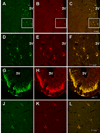
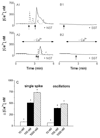
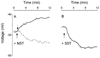
Neuronostatin (NST) is a newly identified peptide of 13-amino acids encoded by the somatostatin (SST) gene. Using a rabbit polyclonal antiserum against the human NST, neuronostatin-immunoreactive (irNST) cells comparable in number and intensity to somatostatin immunoreactive (irSST) cells were detected in the hypothalamic periventricular nucleus. Fewer and/or less intensely labeled irNST cells were noted in other regions such as the hippocampus, cortex, amygdala, and cerebellum. Double-labeling hypothalamic sections with NST- and SST-antiserum revealed an extensive overlapping of irNST and irSST cells in the periventricular nucleus. Pre-absorption of the NST-antiserum with NST (1 microg/ml) but not with SST (1 microg/ml) abrogated irNST and vice versa. The activity of NST on dissociated and cultured hypothalamic neurons was assessed by the Ca(2+) imaging method. NST (10, 100, 1000 nM) concentration-dependently elevated intracellular Ca(2+) concentrations [Ca(2+)](i) in a population of hypothalamic neurons with two distinct profiles: (1) a fast and transitory increase in [Ca(2+)](i), and (2) an oscillatory response. Whereas, SST (100 nM) reduced the basal [Ca(2+)](i) in 21 of 61 hypothalamic neurons examined; an increase was not observed in any of the cells. Optical imaging with a slow-responding voltage sensitive dye DiBAC(4)(3) showed that NST (100 nM) depolarized or hyperpolarized; whereas, SST (100 nM) hyperpolarized a population of hypothalamic neurons. The result shows that NST and SST, though derived from the same precursor protein, exert different calcium mobilizing effects on cultured rat hypothalamic neurons, resulting in diverse cellular activities.
Copyright (c) 2010 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Augustine GJ, Santamaria F, Tanaka K. Local calcium signaling in neurons. Neuron. 2003;40:331–346. - PubMed
-
- Bakhit C, Benoit R, Bloom FE. Release of somatostatin-28(1-12) from rat hypothalamus in vitro. Nature. 1983;301:524–526. - PubMed
-
- Beaudet A, Greenspun D, Raelson J, Tannenbaum GS. Patterns of expression of SSTR1 and SSTR2 somatostatin receptor subtypes in the hypothalamus of the adult rat: relationship to neuroendocrine function. Neurosci. 1995;65:551–561. - PubMed
-
- Bennett GW, Edwardson JA, deCotte DM. Release of somatostatin from rat brain synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1979;32:1127–1130. - PubMed
-
- Benoit R, Bohlen P, Esch F, Ling N. Neuropeptides derived from prosomatostatin that do not contain the somatostatin-14 sequence. Brain Res. 1984;311:23–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

