Expression and function of epithelial anoctamins
- PMID: 20056604
- PMCID: PMC2844227
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.065367
Expression and function of epithelial anoctamins
Abstract
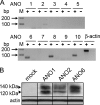
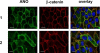
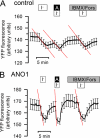
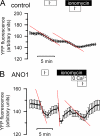
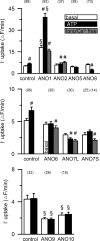
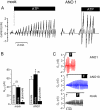
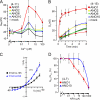
The calcium-activated chloride channel anoctamin1 (ANO1; TMEM16A) is fundamental for the function of epithelial organs. Mice lacking ANO1 expression exhibit transport defects and a pathology similar to cystic fibrosis. They also show a general defect of epithelial electrolyte transport. Here we analyzed expression of all ten members (ANO1-ANO10) in a broad range of murine tissues and detected predominant expression of ANO1, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 in epithelial tissues, while ANO2, 3, 4, 5 are common in neuronal and muscle tissues. When expressed in Fisher Rat Thyroid (FTR) cells, all ANO proteins localized to the plasma membrane but only ANO1, 2, 6, and 7 produced Ca(2+)-activated Cl(-) conductance, as analyzed by ATP-induced iodide quenching of YFP fluorescence. In contrast ANO9 and ANO10 suppressed baseline Cl(-) conductance and coexpression of ANO9 with ANO1 inhibited ANO1 activity. Patch clamping of ANO-expressing FRT cells indicated that apart from ANO1 also ANO6 and 10 produced chloride currents, albeit with very different Ca(2+) sensitivity and activation time. We conclude that each tissue expresses a set of anoctamins that form cell- and tissue-specific Ca(2+)-dependent Cl(-) channels.
Figures



References
-
- Hartzell C., Putzier I., Arreola J. (2005) Annu. Rev. Physiol 67, 719–758 - PubMed
-
- Leblanc N., Ledoux J., Saleh S., Sanguinetti A., Angermann J., O'Driscoll K., Britton F., Perrino B. A., Greenwood I. A. (2005) Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 83, 541–556 - PubMed
-
- Frings S., Reuter D., Kleene S. J. (2000) Prog. Neurobiol. 60, 247–289 - PubMed
-
- Eggermont J. (2004) Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 1, 22–27 - PubMed
-
- Kidd J. F., Thorn P. (2000) Annu. Rev. Physiol. 62, 493–513 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

