Transient and big are key features of an invertebrate T-type channel (LCav3) from the central nervous system of Lymnaea stagnalis
- PMID: 20056611
- PMCID: PMC2844193
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.090753
Transient and big are key features of an invertebrate T-type channel (LCav3) from the central nervous system of Lymnaea stagnalis
Abstract
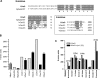
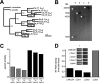
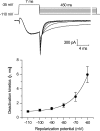
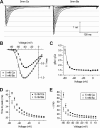
Here we describe features of the first non-mammalian T-type calcium channel (LCa(v)3) expressed in vitro. This molluscan channel possesses combined biophysical properties that are reminiscent of all mammalian T-type channels. It exhibits T-type features such as "transient" kinetics, but the "tiny" label, usually associated with Ba(2+) conductance, is hard to reconcile with the "bigness" of this channel in many respects. LCa(v)3 is 25% larger than any voltage-gated ion channel expressed to date. It codes for a massive, 322-kDa protein that conducts large macroscopic currents in vitro. LCa(v)3 is also the most abundant Ca(2+) channel transcript in the snail nervous system. A window current at typical resting potentials appears to be at least as large as that reported for mammalian channels. This distant gene provides a unique perspective to analyze the structural, functional, drug binding, and evolutionary aspects of T-type channels.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Gene transcription and splicing of T-type channels are evolutionarily-conserved strategies for regulating channel expression and gating.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e37409. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037409. Epub 2012 Jun 15. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22719839 Free PMC article.
-
Gene splicing of an invertebrate beta subunit (LCavβ) in the N-terminal and HOOK domains and its regulation of LCav1 and LCav2 calcium channels.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 1;9(4):e92941. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092941. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24690951 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping of dihydropyridine binding residues in a less sensitive invertebrate L-type calcium channel (LCa v 1).Channels (Austin). 2011 Mar-Apr;5(2):173-87. doi: 10.4161/chan.5.2.15141. Channels (Austin). 2011. PMID: 21487241
-
Three for T: molecular analysis of the low voltage-activated calcium channel family.Cell Mol Life Sci. 1999 Nov 15;56(7-8):660-9. doi: 10.1007/s000180050460. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1999. PMID: 11212313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of the electrophysiological, pharmacological and single channel properties of heart ventricle muscle cells in the snail Lymnaea stagnalis.Experientia. 1992 Sep 15;48(9):841-52. doi: 10.1007/BF02118417. Experientia. 1992. PMID: 1383022 Review.
Cited by
-
Early Metazoan Origin and Multiple Losses of a Novel Clade of RIM Presynaptic Calcium Channel Scaffolding Protein Homologs.Genome Biol Evol. 2020 Aug 1;12(8):1217-1239. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evaa097. Genome Biol Evol. 2020. PMID: 32413100 Free PMC article.
-
NALCN ion channels have alternative selectivity filters resembling calcium channels or sodium channels.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e55088. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055088. Epub 2013 Jan 28. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23383067 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved biophysical features of the CaV2 presynaptic Ca2+ channel homologue from the early-diverging animal Trichoplax adhaerens.J Biol Chem. 2020 Dec 25;295(52):18553-18578. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015725. Epub 2020 Oct 23. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 33097592 Free PMC article.
-
T-type channels become highly permeable to sodium ions using an alternative extracellular turret region (S5-P) outside the selectivity filter.J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 25;289(17):11952-11969. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.551473. Epub 2014 Mar 4. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24596098 Free PMC article.
-
Optimized transfection strategy for expression and electrophysiological recording of recombinant voltage-gated ion channels in HEK-293T cells.J Vis Exp. 2011 Jan 19;(47):2314. doi: 10.3791/2314. J Vis Exp. 2011. PMID: 21304463 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim D., Song I., Keum S., Lee T., Jeong M. J., Kim S. S., McEnery M. W., Shin H. S. (2001) Neuron 31, 35–45 - PubMed
-
- Chemin J., Monteil A., Briquaire C., Richard S., Perez-Reyes E., Nargeot J., Lory P. (2000) FEBS Lett. 478, 166–172 - PubMed
-
- Lory P., Bidaud I., Chemin J. (2006) Cell Calcium 40, 135–146 - PubMed
-
- Shin H. S., Cheong E. J., Choi S., Lee J., Na H. S. (2008) Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 8, 33–41 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

