Quantitative proteomics analysis of cell cycle-regulated Golgi disassembly and reassembly
- PMID: 20056612
- PMCID: PMC2844169
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.047084
Quantitative proteomics analysis of cell cycle-regulated Golgi disassembly and reassembly
Abstract
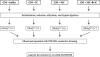
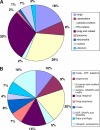
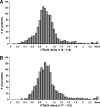
During mitosis, the stacked structure of the Golgi undergoes a continuous fragmentation process. The generated mitotic fragments are evenly distributed into the daughter cells and reassembled into new Golgi stacks. This disassembly and reassembly process is critical for Golgi biogenesis during cell division, but the underlying molecular mechanism is poorly understood. In this study, we have recapitulated this process using an in vitro assay and analyzed the proteins associated with interphase and mitotic Golgi membranes using a proteomic approach. Incubation of purified rat liver Golgi membranes with mitotic HeLa cell cytosol led to fragmentation of the membranes; subsequent treatment of these membranes with interphase cytosol allowed the reassembly of the Golgi fragments into new Golgi stacks. These membranes were then used for quantitative proteomics analyses by combining the isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantification approach with OFFGEL isoelectric focusing separation and liquid chromatography-matrix assisted laser desorption ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. In three independent experiments, a total of 1,193 Golgi-associated proteins were identified and quantified. These included broad functional categories, such as Golgi structural proteins, Golgi resident enzymes, SNAREs, Rab GTPases, cargo, and cytoskeletal proteins. More importantly, the combination of the quantitative approach with Western blotting allowed us to unveil 84 proteins with significant changes in abundance under the mitotic condition compared with the interphase condition. Among these proteins, several COPI coatomer subunits (alpha, beta, gamma, and delta) are of particular interest. Altogether, this systematic quantitative proteomic study revealed candidate proteins of the molecular machinery that control the Golgi disassembly and reassembly processes in the cell cycle.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Quantitative analysis of liver Golgi proteome in the cell cycle.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;909:125-40. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-959-4_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22903713 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstitution of the cell cycle-regulated Golgi disassembly and reassembly in a cell-free system.Nat Protoc. 2010 Apr;5(4):758-72. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2010.38. Epub 2010 Apr 1. Nat Protoc. 2010. PMID: 20360770 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Proteomics Analysis of Purified Rat Liver Golgi.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2557:417-430. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2639-9_25. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36512229 Free PMC article.
-
Golgi architecture and inheritance.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2002;18:379-420. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.18.030602.133733. Epub 2002 Apr 2. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2002. PMID: 12142281 Review.
-
Golgi complex fragmentation in G2/M transition: An organelle-based cell-cycle checkpoint.IUBMB Life. 2012 Aug;64(8):661-70. doi: 10.1002/iub.1054. Epub 2012 Jun 23. IUBMB Life. 2012. PMID: 22730233 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitative analysis of liver Golgi proteome in the cell cycle.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;909:125-40. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-959-4_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22903713 Free PMC article.
-
Mitotic phosphorylation inhibits the Golgi mannosidase MAN1A1.Cell Rep. 2022 Nov 22;41(8):111679. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111679. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 36417860 Free PMC article.
-
Golgi Oncoprotein GOLPH3 Gene Expression Is Regulated by Functional E2F and CREB/ATF Promoter Elements.Genes (Basel). 2019 Mar 25;10(3):247. doi: 10.3390/genes10030247. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30934642 Free PMC article.
-
Combining Mitotic Cell Synchronization and High Resolution Confocal Microscopy to Study the Role of Multifunctional Cell Cycle Proteins During Mitosis.J Vis Exp. 2017 Dec 5;(130):56513. doi: 10.3791/56513. J Vis Exp. 2017. PMID: 29286472 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Chip/Chip/SRM platform using digital chip isoelectric focusing and LC-Chip mass spectrometry for enrichment and quantitation of low abundance protein biomarkers in human plasma.J Proteome Res. 2012 Feb 3;11(2):808-17. doi: 10.1021/pr2006704. Epub 2011 Dec 27. J Proteome Res. 2012. PMID: 22098410 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang Y. (2008) in The Golgi apparatus. State of the Art 110 Years after Camillo Golgi's Discovery (Mironov A., Pavelka M., Luini A. eds.) pp. 580–607, SpringerWeinNewYork, New York
-
- Shorter J., Warren G. (2002) Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 18, 379–420 - PubMed
-
- Liu Z., Vong Q. P., Zheng Y. (2007) Dev. Cell 12, 839–840 - PubMed
-
- Brownhill K., Wood L., Allan V. (2009) Semin Cell Dev. Biol., in press - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

